Role of vision and mechanoreception in bed bug, Cimex lectularius L. behavior
- PMID: 25748041
- PMCID: PMC4351988
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118855
Role of vision and mechanoreception in bed bug, Cimex lectularius L. behavior
Abstract
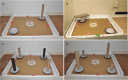
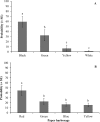
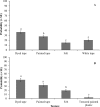
The role of olfactory cues such as carbon dioxide, pheromones, and kairomones in bed bug, Cimex lectularius L. behavior has been demonstrated. However, the role of vision and mechanoreception in bed bug behavior is poorly understood. We investigated bed bug vision by determining their responses to different colors, vertical objects, and their ability to detect colors and vertical objects under low and complete dark conditions. Results show black and red paper harborages are preferred compared to yellow, green, blue, and white harborages. A bed bug trapping device with a black or red exterior surface was significantly more attractive to bed bugs than that with a white exterior surface. Bed bugs exhibited strong orientation behavior toward vertical objects. The height (15 vs. 30 cm tall) and color (brown vs. black) of the vertical object had no significant effect on orientation behavior of bed bugs. Bed bugs could differentiate color and detect vertical objects at very low background light conditions, but not in complete darkness. Bed bug preference to different substrate textures (mechanoreception) was also explored. Bed bugs preferred dyed tape compared to painted tape, textured painted plastic, and felt. These results revealed that substrate color, presence of vertical objects, and substrate texture affect host-seeking and harborage-searching behavior of bed bugs. Bed bugs may use a combination of vision, mechanoreception, and chemoreception to locate hosts and seek harborages.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Allan SA, Day JF, Edman JD (1987) Visual ecology of biting flies. Annu Rev Entomol 32: 297–316. - PubMed
-
- Lehane MJ (1991) Biology of blood-sucking insects In: Lehane MJ, editor. London: Harper Collins Academic; pp. 288.
-
- Anderson JF, Ferrandino FJ, McKnight S, Nolen J, Miller J (2009) A carbon dioxide, heat and chemical lure trap for the bed bug, Cimex lectularius. Med Vet Entomol 23: 99–105. - PubMed
-
- Wang C, Gibb T, Bennett GW, McKnight S (2009) Bed bug (Heteroptera: Cimicidae) attraction to pitfall traps baited with carbon dioxide, heat and chemical lure. J Econ Entomol 102: 1580–1585. - PubMed
-
- Singh N, Wang C, Cooper R (2012) Interactions among non-chemical and chemical lures in attracting the bed bug, Cimex lectularius L. (Hemiptera: Cimicidae). Psyche. doi: 10.1155/2012/273613. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

