A map of directional genetic interactions in a metazoan cell
- PMID: 25748138
- PMCID: PMC4384530
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.05464
A map of directional genetic interactions in a metazoan cell
Abstract
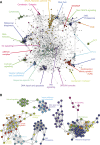
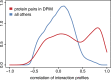
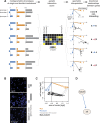
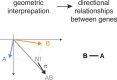
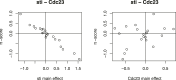
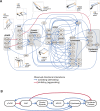
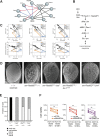
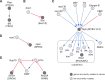
Gene-gene interactions shape complex phenotypes and modify the effects of mutations during development and disease. The effects of statistical gene-gene interactions on phenotypes have been used to assign genes to functional modules. However, directional, epistatic interactions, which reflect regulatory relationships between genes, have been challenging to map at large-scale. Here, we used combinatorial RNA interference and automated single-cell phenotyping to generate a large genetic interaction map for 21 phenotypic features of Drosophila cells. We devised a method that combines genetic interactions on multiple phenotypes to reveal directional relationships. This network reconstructed the sequence of protein activities in mitosis. Moreover, it revealed that the Ras pathway interacts with the SWI/SNF chromatin-remodelling complex, an interaction that we show is conserved in human cancer cells. Our study presents a powerful approach for reconstructing directional regulatory networks and provides a resource for the interpretation of functional consequences of genetic alterations.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; chromosomes; epistasis; evolutionary biology; genes; genetic interactions; genomics; image-based phenotyping.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Babu M, Arnold R, Bundalovic-Torma C, Gagarinova A, Wong KS, Kumar A, Stewart G, Samanfar B, Aoki H, Wagih O, Vlasblom J, Phanse S, Lad K, Yeou Hsiung Yu A, Graham C, Jin K, Brown E, Golshani A, Kim P, Moreno-Hagelsieb G, Greenblatt J, Houry WA, Parkinson J, Emili A. Quantitative genome-wide genetic interaction screens reveal global epistatic relationships of protein complexes in Escherichia coli. PLOS Genetics. 2014;10:e1004120. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004120. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bassik MC, Kampmann M, Lebbink RJ, Wang S, Hein MY, Poser I, Weibezahn J, Horlbeck MA, Chen S, Mann M, Hyman AA, Leproust EM, McManus MT, Weissman JS. A systematic mammalian genetic interaction map reveals pathways underlying ricin susceptibility. Cell. 2013;152:909–922. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.01.030. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

