The Sordid Affair Between Human Herpesvirus and HIV
- PMID: 25748324
- PMCID: PMC4548466
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiv148
The Sordid Affair Between Human Herpesvirus and HIV
Abstract
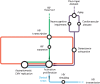
Both human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and human herpesvirus (HHV) infections persist lifelong, and almost all individuals infected with HIV are also infected with ≥1 HHV. These coinfections are not independent processes or benign. In this review, we discuss how HHVs, and cytomegalovirus in particular, interact with concurrent HIV infection, and we describe the next steps necessary to understand and address these connections.
Keywords: HIV; Human herpesvirus; cytomegalovirus; epidemiology transmission; inflammation; pathogenesis.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Van de Perre P, Segondy M, Foulongne V, et al. Herpes simplex virus and HIV-1: deciphering viral synergy. Lancet Infect Dis 2008; 8:490–7. - PubMed
-
- McGeoch DJ, Cook S, Dolan A, Jamieson FE, Telford EA. Molecular phylogeny and evolutionary timescale for the family of mammalian herpesviruses. J Mol Biol 1995; 247:443–58. - PubMed
-
- Griffiths PD. CMV as a cofactor enhancing progression of AIDS. J Clin Virol 2006; 35:489–92. - PubMed
-
- Webster A, Lee CA, Cook DG, et al. Cytomegalovirus infection and progression towards AIDS in haemophiliacs with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Lancet 1989; 2:63–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- K24 AI100665/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 7-UM1 AI068636-07/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI074621/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI036214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MH097520/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI043638/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007384/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 DA034978/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- AI110181/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DA034978/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI100665/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI007384/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI110181/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000100/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH097520/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AI43638/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI106039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI074621/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000100/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH100974/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AI106039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

