Genetic risk, coronary heart disease events, and the clinical benefit of statin therapy: an analysis of primary and secondary prevention trials
- PMID: 25748612
- PMCID: PMC4608367
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61730-X
Genetic risk, coronary heart disease events, and the clinical benefit of statin therapy: an analysis of primary and secondary prevention trials
Abstract
Background: Genetic variants have been associated with the risk of coronary heart disease. In this study, we tested whether or not a composite of these variants could ascertain the risk of both incident and recurrent coronary heart disease events and identify those individuals who derive greater clinical benefit from statin therapy.
Methods: A community-based cohort study (the Malmo Diet and Cancer Study) and four randomised controlled trials of both primary prevention (JUPITER and ASCOT) and secondary prevention (CARE and PROVE IT-TIMI 22) with statin therapy, comprising a total of 48,421 individuals and 3477 events, were included in these analyses. We studied the association of a genetic risk score based on 27 genetic variants with incident or recurrent coronary heart disease, adjusting for traditional clinical risk factors. We then investigated the relative and absolute risk reductions in coronary heart disease events with statin therapy stratified by genetic risk. We combined data from the different studies using a meta-analysis.
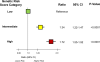
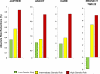
Findings: When individuals were divided into low (quintile 1), intermediate (quintiles 2-4), and high (quintile 5) genetic risk categories, a significant gradient in risk for incident or recurrent coronary heart disease was shown. Compared with the low genetic risk category, the multivariable-adjusted hazard ratio for coronary heart disease for the intermediate genetic risk category was 1·34 (95% CI 1·22-1·47, p<0·0001) and that for the high genetic risk category was 1·72 (1·55-1·92, p<0·0001). In terms of the benefit of statin therapy in the four randomised trials, we noted a significant gradient (p=0·0277) of increasing relative risk reductions across the low (13%), intermediate (29%), and high (48%) genetic risk categories. Similarly, we noted greater absolute risk reductions in those individuals in higher genetic risk categories (p=0·0101), resulting in a roughly threefold decrease in the number needed to treat to prevent one coronary heart disease event in the primary prevention trials. Specifically, in the primary prevention trials, the number needed to treat to prevent one such event in 10 years was 66 in people at low genetic risk, 42 in those at intermediate genetic risk, and 25 in those at high genetic risk in JUPITER, and 57, 47, and 20, respectively, in ASCOT.
Interpretation: A genetic risk score identified individuals at increased risk for both incident and recurrent coronary heart disease events. People with the highest burden of genetic risk derived the largest relative and absolute clinical benefit from statin therapy.
Funding: National Institutes of Health.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Statin treatment: can genetics sharpen the focus?Lancet. 2015 Jun 6;385(9984):2227-9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61931-0. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Lancet. 2015. PMID: 25748613 No abstract available.
-
Genetics: Genetic risk scores--new promises for drug evaluation.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015 Jun;12(6):321-2. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.62. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25898262 No abstract available.
-
[Less (pulmonary embolism) recurrence through longer oral anticoagulation].Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2015 Sep;140(19):1416. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-103233. Epub 2015 Sep 24. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2015. PMID: 26402171 German. No abstract available.
References
-
- Marenberg ME, Risch N, Berkman LF, Floderus B, de Faire U. Genetic susceptibility to death from coronary heart disease in a study of twins. N Engl J Med. 1994;330(15):1041–6. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones DM, Nam BH, D'Agostino RB, Sr., Levy D, Murabito JM, Wang TJ, et al. Parental cardiovascular disease as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease in middle-aged adults: a prospective study of parents and offspring. Jama. 2004;291(18):2204–11. - PubMed
-
- Humphries SE, Cooper JA, Talmud PJ, Miller GJ. Candidate gene genotypes, along with conventional risk factor assessment, improve estimation of coronary heart disease risk in healthy UK men. Clinical chemistry. 2007;53(1):8–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

