Hypothalamic Agrp neurons drive stereotypic behaviors beyond feeding
- PMID: 25748653
- PMCID: PMC4484787
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.02.024
Hypothalamic Agrp neurons drive stereotypic behaviors beyond feeding
Erratum in
-
Hypothalamic Agrp Neurons Drive Stereotypic Behaviors beyond Feeding.Cell. 2017 Apr 20;169(3):559. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.04.006. Cell. 2017. PMID: 28431254 No abstract available.
Abstract
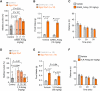
The nervous system evolved to coordinate flexible goal-directed behaviors by integrating interoceptive and sensory information. Hypothalamic Agrp neurons are known to be crucial for feeding behavior. Here, however, we show that these neurons also orchestrate other complex behaviors in adult mice. Activation of Agrp neurons in the absence of food triggers foraging and repetitive behaviors, which are reverted by food consumption. These stereotypic behaviors that are triggered by Agrp neurons are coupled with decreased anxiety. NPY5 receptor signaling is necessary to mediate the repetitive behaviors after Agrp neuron activation while having minor effects on feeding. Thus, we have unmasked a functional role for Agrp neurons in controlling repetitive behaviors mediated, at least in part, by neuropeptidergic signaling. The findings reveal a new set of behaviors coupled to the energy homeostasis circuit and suggest potential therapeutic avenues for diseases with stereotypic behaviors.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
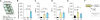

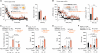



References
-
- Anderson DJ, Perona P. Toward a science of computational ethology. Neuron. 2014;84:18–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

