Skeletal muscle signature of a champion sprint runner
- PMID: 25749440
- PMCID: PMC4469925
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00037.2015
Skeletal muscle signature of a champion sprint runner
Abstract
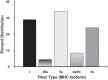
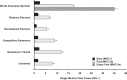
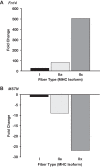
We had the unique opportunity to study the skeletal muscle characteristics, at the single fiber level, of a world champion sprint runner who is the current indoor world record holder in the 60-m hurdles (7.30 s) and former world record holder in 110-m hurdles (12.91 s). Muscle biopsies were obtained from the vastus lateralis at rest and 4 h after a high-intensity exercise challenge (4 × 7 repetitions of resistance exercise). Single muscle fiber analyses were conducted for fiber type distribution (myosin heavy chain, MHC), fiber size, contractile function (strength, speed, and power) and mRNA expression (before and after the exercise bout). The world-class sprinter's leg muscle had a high abundance (24%) of the pure MHC IIx muscle fibers with a total fast-twitch fiber population of 71%. Power output of the MHC IIx fibers (35.1 ± 1.4 W/l) was 2-fold higher than MHC IIa fibers (17.1 ± 0.5 W/l) and 14-fold greater than MHC I fibers (2.5 ± 0.1 W/l). Additionally, the MHC IIx fibers were highly responsive to intense exercise at the transcriptional level for genes involved with muscle growth and remodeling (Fn14 and myostatin). To our knowledge, the abundance of pure MHC IIx muscle fibers is the highest observed in an elite sprinter. Further, the power output of the MHC IIa and MHC IIx muscle fibers was greater than any human values reported to date. These data provide a myocellular basis for the high level of sprinting success achieved by this individual.
Keywords: athlete; fiber type; gene expression; performance; single muscle fiber.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Invited Editorial on "Skeletal Muscle Signature of a Champion Sprint Runner".J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015 Jun 15;118(12):1447-8. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00102.2015. Epub 2015 Apr 24. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015. PMID: 25911682 No abstract available.
-
Exceptional case studies.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015 Jun 15;118(12):1449. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00269.2015. Epub 2015 Apr 24. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015. PMID: 25911683 No abstract available.
References
-
- Alkner BA, Tesch PA. Efficacy of a gravity-independent resistance exercise device as a countermeasure to muscle atrophy during 29-day bed rest. Acta Physiol Scand 181: 345–357, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Andersen JL, Klitgaard H, Bangsbo J, Saltin B. Myosin heavy chain isoforms in single fibres from m. vastus lateralis of soccer players: effects of strength-training. Acta Physiol Scand 150: 21–26, 1994. - PubMed
-
- Andersen JL, Klitgaard H, Saltin B. Myosin heavy chain isoforms in single fibres from m. vastus lateralis of sprinters: influence of training. Acta Physiol Scand 151: 135–142, 1994. - PubMed
-
- Andersen JL, Mohr T, Biering-Sorensen F, Galbo H, Kjaer M. Myosin heavy chain isoform transformation in single fibres from m. vastus lateralis in spinal cord injured individuals: effects of long-term functional electrical stimulation (FES). Pflügers Arch 431: 513–518, 1996. - PubMed
-
- Bergstrom J. Muscle electrolytes in man. Scan J Clin Lab Invest 68: 1–110, 1962.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

