Salmonellae interactions with host processes
- PMID: 25749450
- PMCID: PMC5074537
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro3420
Salmonellae interactions with host processes
Abstract
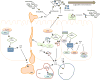
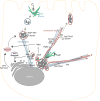
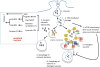
Salmonellae invasion and intracellular replication within host cells result in a range of diseases, including gastroenteritis, bacteraemia, enteric fever and focal infections. In recent years, considerable progress has been made in our understanding of the molecular mechanisms that salmonellae use to alter host cell physiology; through the delivery of effector proteins with specific activities and through the modulation of defence and stress response pathways. In this Review, we summarize our current knowledge of the complex interplay between bacterial and host factors that leads to inflammation, disease and, in most cases, control of the infection by its animal hosts, with a particular focus on Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium. We also highlight gaps in our knowledge of the contributions of salmonellae and the host to disease pathogenesis, and we suggest future avenues for further study.
Figures

References
-
- Pegues DA, Ohl ME, Miller SI. In: Salmonella species, including Salmonella typhi. Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R, editors. Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone; New York: 2005.
-
- Harris JC, Dupont HL, Hornick RB. Fecal leukocytes in diarrheal illness. Ann Intern Med. 1972;76:697–703. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

