Insights into copper coordination in the EcoRI-DNA complex by ESR spectroscopy
- PMID: 25750461
- PMCID: PMC4350447
- DOI: 10.1080/00268976.2014.934313
Insights into copper coordination in the EcoRI-DNA complex by ESR spectroscopy
Abstract
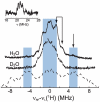
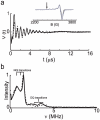
The EcoRI restriction endonuclease requires one divalent metal ion in each of two symmetrical and identical catalytic sites to catalyse double-strand DNA cleavage. Recently, we showed that Cu2+ binds outside the catalytic sites to a pair of new sites at H114 in each sub-unit, and inhibits Mg2+ -catalysed DNA cleavage. In order to provide more detailed structural information on this new metal ion binding site, we performed W-band (~94 GHz) and X-band (~9.5 GHz) electron spin resonance spectroscopic measurements on the EcoRI-DNA-(Cu2+ )2 complex. Cu2+ binding results in two distinct components with different gzz and Azz values. X-band electron spin echo envelope modulation results indicate that both components arise from a Cu2+ coordinated to histidine. This observation is further confirmed by the hyperfine sub-level correlation results. W-band electron nuclear double resonance spectra provide evidence for equatorial coordination of water molecules to the Cu2+ ions.
Keywords: Cu2+ inhibition; ESEEM; W-band ENDOR; metal ion coordination; restriction endonuclease.
Figures


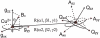




References
-
- Lesser DR, Kurpiewski MR, Jen-Jacobson L. Science. 1990;250(776) - PubMed
-
- Sapienza PJ, dela Torre CA, McCoy WH, IV, Jana SV, Jen-Jacobson L. J. Mol. Biol. 2005;348(307) - PubMed
-
- Kurpiewski MR, Engler LE, Wozniak LA, Kobylanska A, Koziolkiewicz M, Stec WJ, Jen-Jacobson L. Structure. 2004;12(1775) - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
