Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review
- PMID: 25750745
- PMCID: PMC4348459
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2013.07.006
Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review
Abstract
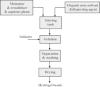
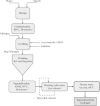
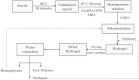
Hydrogel products constitute a group of polymeric materials, the hydrophilic structure of which renders them capable of holding large amounts of water in their three-dimensional networks. Extensive employment of these products in a number of industrial and environmental areas of application is considered to be of prime importance. As expected, natural hydrogels were gradually replaced by synthetic types due to their higher water absorption capacity, long service life, and wide varieties of raw chemical resources. Literature on this subject was found to be expanding, especially in the scientific areas of research. However, a number of publications and technical reports dealing with hydrogel products from the engineering points of view were examined to overview technological aspects covering this growing multidisciplinary field of research. The primary objective of this article is to review the literature concerning classification of hydrogels on different bases, physical and chemical characteristics of these products, and technical feasibility of their utilization. It also involved technologies adopted for hydrogel production together with process design implications, block diagrams, and optimized conditions of the preparation process. An innovated category of recent generations of hydrogel materials was also presented in some details.
Keywords: Hydrogel; Innovation; Optimization; Preparation; Processing.
Figures









References
-
- Ahmed Enas M., Aggor Fatma S., Awad Ahmed M., El-Aref Ahmed T. An innovative method for preparation of nanometal hydroxide superabsorbent hydrogel. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;91:693–698. - PubMed
-
- Buchholz F.L., Graham A.T. Wiley- VCH; New York: 1998. Modern superabsorbent polymer technology. [chapters 1–7]
-
- Brannon-Peppas L., Harland R.S. Absorbent polymer technology. J Controlled Release. 1991;17(3):297–298.
-
- Li Yuhui, Huang Guoyou, Zhang Xiaohui, Li Baoqiang, Chen Yongmei, Lu Tingli, Lu Tian Jian, Xu Feng. Magnetic hydrogels and their potential biomedical applications. Adv Funct Mater. 2013;23(6):660–672.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

