Integrin α3β1 signaling through MEK/ERK determines alternative polyadenylation of the MMP-9 mRNA transcript in immortalized mouse keratinocytes
- PMID: 25751421
- PMCID: PMC4353714
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119539
Integrin α3β1 signaling through MEK/ERK determines alternative polyadenylation of the MMP-9 mRNA transcript in immortalized mouse keratinocytes
Abstract
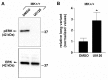
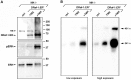
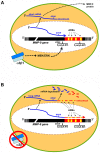
Integrin α3β1 is highly expressed in both normal and tumorigenic epidermal keratinocytes where it regulates genes that control cellular function and extracellular matrix remodeling during normal and pathological tissue remodeling processes, including wound healing and development of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Previous studies identified a role for α3β1 in immortalized and transformed keratinocytes in the regulation of genes that promote tumorigenesis, invasion, and pro-angiogenic crosstalk to endothelial cells. One such gene, matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), is induced by α3β1 through a post-transcriptional mechanism of enhanced mRNA stability. In the current study, we sought to investigate the mechanism through which α3β1 controls MMP-9 mRNA stability. First, we utilized a luciferase reporter assay to show that AU-rich elements (AREs) residing within the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of the MMP-9 mRNA renders the transcript unstable in a manner that is independent of α3β1. Next, we cloned a truncated variant of the MMP-9 mRNA which is generated through usage of an alternative, upstream polyadenylation signal and lacks the 3'-UTR region containing the destabilizing AREs. Using an RNase protection assay to distinguish "long" (full-length 3'-UTR) and "short" (truncated 3'-UTR) MMP-9 mRNA variants, we demonstrated that the shorter, more stable mRNA that lacks 3'-UTR AREs was preferentially generated in α3β1-expressing keratinocytes compared with α3β1-deficient (i.e., α3-null) keratinocytes. Moreover, we determined that α3β1-dependent alternative polyadenylation was acquired by immortalized keratinocytes, as primary neonatal keratinocytes did not display α3β1-dependent differences in the long and short transcripts. Finally, pharmacological inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway in α3β1-expressing keratinocytes caused a shift towards long variant expression, while Raf-1-mediated activation of ERK in α3-null keratinocytes dramatically enhanced short variant expression, indicating a role for ERK/MAPK signaling in α3β1-mediated selection of the proximal polyadenylation site. These findings identify a novel mode of integrin α3β1-mediated gene regulation through alternative polyadenylation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
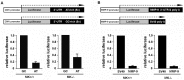
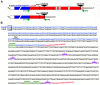
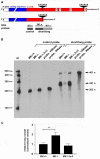
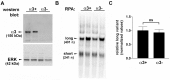
References
-
- Kreidberg JA. Functions of α3β1 integrin. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2000;12: 548–553. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

