Structural basis for VEGF-C binding to neuropilin-2 and sequestration by a soluble splice form
- PMID: 25752543
- PMCID: PMC4394031
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2015.01.018
Structural basis for VEGF-C binding to neuropilin-2 and sequestration by a soluble splice form
Abstract
Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) is a potent lymphangiogenic cytokine that signals via the coordinated action of two cell surface receptors, Neuropilin-2 (Nrp2) and VEGFR-3. Diseases associated with both loss and gain of VEGF-C function, lymphedema and cancer, respectively, motivate studies of VEGF-C/Nrp2 binding and inhibition. Here, we demonstrate that VEGF-C binding to Nrp2 is regulated by C-terminal proteolytic maturation. The structure of the VEGF-C C terminus in complex with the ligand binding domains of Nrp2 demonstrates that a cryptic Nrp2 binding motif is released upon proteolysis, allowing specific engagement with the b1 domain of Nrp2. Based on the identified structural requirements for Nrp2 binding to VEGF-C, we hypothesized that the endogenous secreted splice form of Nrp2, s9Nrp2, may function as a selective inhibitor of VEGF-C. We find that s9Nrp2 forms a stable dimer that potently inhibits VEGF-C/Nrp2 binding and cellular signaling. These data provide critical insight into VEGF-C/Nrp2 binding and inhibition.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

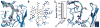
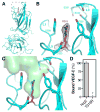

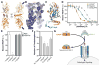
Comment in
-
Splicing and proteolytic processing in VEGF signaling: now it is the coreceptor's turn.Structure. 2015 Apr 7;23(4):610-1. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2015.03.003. Structure. 2015. PMID: 25862932
References
-
- Aricescu AR, Lu W, Jones EY. A time- and cost-efficient system for high-level protein production in mammalian cells. Acta Crystallogr D, Biol Crystallogr. 2006;62:1243–1250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

