Fatty acid trafficking in starved cells: regulation by lipid droplet lipolysis, autophagy, and mitochondrial fusion dynamics
- PMID: 25752962
- PMCID: PMC4375018
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.01.029
Fatty acid trafficking in starved cells: regulation by lipid droplet lipolysis, autophagy, and mitochondrial fusion dynamics
Abstract
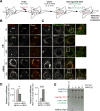
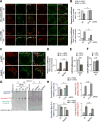
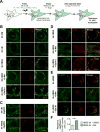
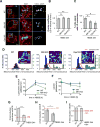
Fatty acids (FAs) provide cellular energy under starvation, yet how they mobilize and move into mitochondria in starved cells, driving oxidative respiration, is unclear. Here, we clarify this process by visualizing FA trafficking with a fluorescent FA probe. The labeled FA accumulated in lipid droplets (LDs) in well-fed cells but moved from LDs into mitochondria when cells were starved. Autophagy in starved cells replenished LDs with FAs, increasing LD number over time. Cytoplasmic lipases removed FAs from LDs, enabling their transfer into mitochondria. This required mitochondria to be highly fused and localized near LDs. When mitochondrial fusion was prevented in starved cells, FAs neither homogeneously distributed within mitochondria nor became efficiently metabolized. Instead, FAs reassociated with LDs and fluxed into neighboring cells. Thus, FAs engage in complex trafficking itineraries regulated by cytoplasmic lipases, autophagy, and mitochondrial fusion dynamics, ensuring maximum oxidative metabolism and avoidance of FA toxicity in starved cells.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

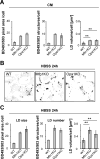
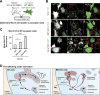
Comment in
-
Lipid metabolism: fatty acids on the move.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Apr;16(4):204. doi: 10.1038/nrm3972. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25785715 No abstract available.
-
Fatty acid metabolism meets organelle dynamics.Dev Cell. 2015 Mar 23;32(6):657-8. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.03.008. Dev Cell. 2015. PMID: 25805129
References
-
- Axe EL, Walker SA, Manifava M, Chandra P, Roderick HL, Habermann A, Griffiths G, Ktistakis NT. Autophagosome formation from membrane compartments enriched in phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and dynamically connected to the endoplasmic reticulum. The Journal of cell biology. 2008;182:685–701. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Calder PC. Long chain fatty acids and gene expression in inflammation and immunity. Current opinion in clinical nutrition and metabolic care. 2013;16:425–433. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Chomyn A, Chan DC. Disruption of fusion results in mitochondrial heterogeneity and dysfunction. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2005;280:26185–26192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

