Visualization of synaptic domains in the Drosophila brain by magnetic resonance microscopy at 10 micron isotropic resolution
- PMID: 25753480
- PMCID: PMC4649768
- DOI: 10.1038/srep08920
Visualization of synaptic domains in the Drosophila brain by magnetic resonance microscopy at 10 micron isotropic resolution
Abstract
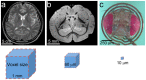
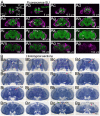
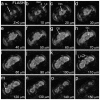
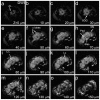
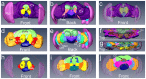
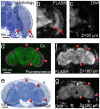
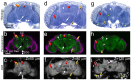
Understanding the complex architecture, connectivity, and pathology of the human brain is a major application of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). However, the cellular basis of MR signal is still poorly understood. The advent of MR microscopy (MRM) enables imaging biological samples at cellular resolution, helping to interpret the nature of MR signal at the cellular level. In this regard, the small Drosophila brain can reveal key aspects of MR signal through the visualization of complex, intact neuronal structures in their native spatial arrangement. Applying state-of-the-art MR technology, we imaged fixed Drosophila heads at 10 μm isotropic resolution by two endogenously contrasted MRM sequences. The improved MRM sensitivity described here delivered the highest 3D resolution of an intact animal head reported so far. 3D fast low angle shot (FLASH) revealed strong signal in most internal tissues, particularly in the brain cortex, which contains the cell bodies of neurons and glia. Remarkably, 3D diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) delivered unprecedented contrast within the modular brain neuropil, revealing hyperintense signal in synapse-rich microdomains. Thus, the complex Drosophila brain revealed unknown features of FLASH and DWI with potential applications in characterizing the structure and pathology of the mammalian brain.
Figures
References
-
- Lauterbur P. C. Image formation by induced local interactions: examples employing nuclear magnetic resonance. Nature 242, 190–191 (1973). - PubMed
-
- Eccles C. & Callaghan P. High resolution imaging: the NMR microscope. J Magn Reson 68, 393–398 (1986).
-
- Johnson G., Thompson M. G., L. S. & Hayes C. Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging at microscopic resolution. J Magn Reson 68, 129–137 (1986).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

