Metabolic study of Angelica dahurica extracts using a reusable liver microsomal nanobioreactor by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
- PMID: 25753568
- PMCID: PMC4562904
- DOI: 10.1002/bmc.3451
Metabolic study of Angelica dahurica extracts using a reusable liver microsomal nanobioreactor by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
Abstract
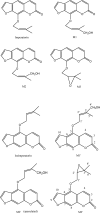
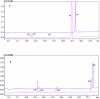
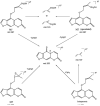
Highly active and recoverable nanobioreactors prepared by immobilizing rat liver microsomes on magnetic nanoparticles (LMMNPs) were utilized in metabolic study of Angelica dahurica extracts. Five metabolites were detected in the incubation solution of the extracts and LMMNPs, which were identified by means of HPLC-MS as trans-imperatorin hydroxylate (M1), cis-imperatorin hydroxylate (M2), imperatorin epoxide (M3), trans-isoimperatorin hydroxylate (M1') and cis-isoimperatorin hydroxylate (speculated M2'). Compared with the metabolisms of imperatorin and isoimperatorin, it was found that the five metabolites were all transformed from these two major compounds present in the plant. Since no study on isoimperatorin metabolism by liver microsomal enzyme system has been reported so far, its metabolites (M1' and M3') were isolated by preparative HPLC for structure elucidation by (1) H-NMR and MS(2) analysis. M3' was identified as isoimperatorin epoxide, which is a new compound as far as its chemical structure is concerned. However, interestingly, M3' was not detected in the metabolism of the whole plant extract. In addition, a study with known chemical inhibitors on individual isozymes of the microsomal enzyme family revealed that CYP1A2 is involved in metabolisms of both isoimperatorin and imperatorin, and CYP3A4 only in that of isoimperatorin.
Keywords: Angelica dahurica; HPLC-MS; furocoumarins; immobilized liver microsomes; magnetic nanoparticles; metabolites.
Copyright © 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures

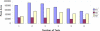

References
-
- Bajrami B, Hvastkovs EG, Jensen GC, Schenkman JB, Rusling JF. Enzyme-DNA biocolloids for DNA adduct and reactive metabolite detection by chromatography-mass Spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2008;80:922–932. - PubMed
-
- Ban HS, Lim SS, Suzuki K, Jung SH, Lee S, Lee YS, Shin KH, Ohuchi K. Inhibitory effects of furanocoumarins isolated from the roots of Angelica dahurica on prostaglandin E-2 production. Planta Med. 2003;69:408–412. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. Rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Dasgupta D, Tang W, Caldwell GW, Yan Z. Use of stable isotope labeled probes to facilitate liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry based high-throughput screening of time-dependent CYP inhibitors. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2010;24:2177–2185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

