Sphingolipids as cell fate regulators in lung development and disease
- PMID: 25753687
- PMCID: PMC4376961
- DOI: 10.1007/s10495-015-1112-6
Sphingolipids as cell fate regulators in lung development and disease
Abstract
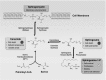
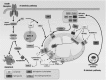
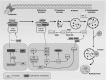
Sphingolipids are a diverse class of signaling molecules implicated in many important aspects of cellular biology, including growth, differentiation, apoptosis, and autophagy. Autophagy and apoptosis are fundamental physiological processes essential for the maintenance of cellular and tissue homeostasis. There is great interest into the investigation of sphingolipids and their roles in regulating these key physiological processes as well as the manifestation of several disease states. With what is known to date, the entire scope of sphingolipid signaling is too broad, and a single review would hardly scratch the surface. Therefore, this review attempts to highlight the significance of sphingolipids in determining cell fate (e.g. apoptosis, autophagy, cell survival) in the context of the healthy lung, as well as various respiratory diseases including acute lung injury, acute respiratory distress syndrome, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, emphysema, and cystic fibrosis. We present an overview of the latest findings related to sphingolipids and their metabolites, provide a short introduction to autophagy and apoptosis, and then briefly highlight the regulatory roles of sphingolipid metabolites in switching between cell survival and cell death. Finally, we describe functions of sphingolipids in autophagy and apoptosis in lung homeostasis, especially in the context of the aforementioned diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sphingolipids in the lungs.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008 Dec 1;178(11):1100-14. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200804-595SO. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008. PMID: 18755926
-
Sphingolipids in lung growth and repair.Chest. 2014 Jan;145(1):120-128. doi: 10.1378/chest.13-0967. Chest. 2014. PMID: 24394822 Review.
-
Bioactive Sphingolipids in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018 Dec;15(Suppl 4):S249-S252. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201809-592MG. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018. PMID: 30759004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ceramide Signaling and Metabolism in Pathophysiological States of the Lung.Annu Rev Physiol. 2016;78:463-80. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021115-105221. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Annu Rev Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26667073 Review.
-
Sphingolipids: regulators of crosstalk between apoptosis and autophagy.J Lipid Res. 2013 Jan;54(1):5-19. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R031278. Epub 2012 Nov 13. J Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23152582 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New Pharmacologic Approaches to Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia.J Exp Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 25;13:377-396. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S262350. eCollection 2021. J Exp Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33790663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum Sphingolipids Aiding the Diagnosis of Adult HIV-Negative Patients with Talaromyces marneffei Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Jun 28;11:701913. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.701913. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34262882 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperoxic Exposure Caused Lung Lipid Compositional Changes in Neonatal Mice.Metabolites. 2020 Aug 21;10(9):340. doi: 10.3390/metabo10090340. Metabolites. 2020. PMID: 32825609 Free PMC article.
-
Ceramides, Autophagy, and Apoptosis Mechanisms of Ventilator-induced Lung Injury and Potential Therapeutic Targets.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Mar 15;199(6):687-689. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201810-1857ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019. PMID: 30372122 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Metabolomic profiling of human pluripotent stem cell differentiation into lung progenitors.iScience. 2022 Jan 20;25(2):103797. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.103797. eCollection 2022 Feb 18. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35198866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spiegel S, Foster D, Kolesnick R. Signal transduction through lipid second messengers. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996;8:159–167. - PubMed
-
- Yang Y, Uhlig S. The role of sphingolipids in respiratory disease. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2011;5:325–344. - PubMed
-
- Spiegel S, Milstien S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate: an enigmatic signalling lipid. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:397–407. - PubMed
-
- Liu H, Chakravarty D, Maceyka M, et al. Sphingosine kinases: a novel family of lipid kinases. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2002;71:493–511. - PubMed
-
- Kolesnick RN, Krönke M. Regulation of ceramide production and apoptosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1998;60:643–665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

