A randomised controlled trial of a brief cognitive behavioural intervention for men who have hot flushes following prostate cancer treatment (MANCAN)
- PMID: 25753889
- PMCID: PMC5006840
- DOI: 10.1002/pon.3794
A randomised controlled trial of a brief cognitive behavioural intervention for men who have hot flushes following prostate cancer treatment (MANCAN)
Abstract
Objective: Hot flushes and night sweats (HFNS) are experienced by up to 80% of prostate cancer patients undergoing androgen deprivation therapy (ADT). This study evaluates the effects of a guided self-help cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) intervention on HFNS problem-rating (primary outcome), HFNS frequency, mood and health-related quality of life (secondary outcomes) in patients undergoing ADT.
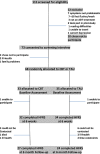
Methods: Patients reporting treatment-induced HFNS were randomly assigned to CBT (n = 33) or treatment as usual (TAU) (n = 35), stratified for cancer type. The CBT intervention included a booklet, CD plus telephone contact during a 4-week period. Validated self-report questionnaires were completed at baseline, 6 weeks and 32 weeks after randomisation. The primary outcome was HFNS problem rating (perceived burden of HFNS) at 6 weeks after randomisation. Potential moderators and mediators were examined. Data analysis was conducted on a modified intention-to-treat basis.
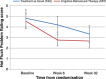
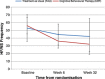
Results: Compared with TAU, CBT significantly reduced HFNS problem rating (adjusted mean difference: -1.33, 95% CI -2.07 to -0.58; p = 0.001) and HFNS frequency (-12.12, 95% CI -22.39 to -1.84; p = 0.02) at 6 weeks. Improvements were maintained at 32 weeks, but group differences did not reach significance. There were significant reductions in negative HFNS Beliefs and Behaviours following CBT, but not in mood or quality of life.
Conclusions: Guided self-help CBT appears to be a safe and effective brief treatment for men who have problematic HFNS following prostate cancer treatments. Further research might test the efficacy of the intervention in a multicentre trial.
© 2015 The Authors. Psycho-Oncology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA: A Cancer J Clin 2011;61(2):69–90. - PubMed
-
- Grunfeld EA, Halliday A, Martin P, et al. Andropause syndrome in men treated for metastatic prostate cancer: a qualitative study of the impact of symptoms. Cancer Nurs. 2013;35(1):63–69. - PubMed
-
- Frisk J. Managing hot flushes in men after prostate cancer. A systematic review. Maturitas 2010;65(1):15–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

