Characterization of HIV drug resistance mutations among patients failing first-line antiretroviral therapy from a tertiary referral center in Lusaka, Zambia
- PMID: 25754408
- PMCID: PMC4489546
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.24162
Characterization of HIV drug resistance mutations among patients failing first-line antiretroviral therapy from a tertiary referral center in Lusaka, Zambia
Abstract
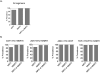
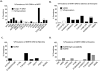
In settings of resource constraint, an understanding of HIV drug resistance can guide antiretroviral therapy (ART) at switch to second-line therapy. To determine the prevalence of such HIV drug resistance mutations (HIV DRM), we used an in-house sequencing assay in the pol gene (protease and partial reverse transcriptase) in a cohort of patients suspected of failing a first-line regimen, which in Zambia comprises two nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) and one non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI). Our analysis cohort (n = 68) was referred to the University Teaching Hospital in Lusaka from November 2009 to October 2012. Median duration on first-line ART to suspected treatment failure was 3.2 years (IQR 1.7-4.7 years). The majority of patients (95%) harbored HIV-1 subtype C virus. Analysis of reverse transcriptase revealed M184V (88%), K103N/S (32%), and Y181C/I/V (41%) DRMs, with the latter conferring reduced susceptibility to the salvage therapy candidates etravirine and rilpivirine. Three patients (5%) had major protease inhibitor (PI) resistance mutations: all three had the V82A mutation, and one patient (Clade J virus) had a concurrent M46I, Q58E, and L76V DRM. HIV-1 genotyping revealed major and minor DRMs as well as high levels of polymorphisms in subtype C isolates from patients failing first-line antiretroviral therapy. Closer monitoring of DRM mutations at first-line failure can inform clinicians about future options for salvage therapy.
Keywords: HIV drug resistance; NNRTI; Zambia; diversity; pol.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Bennett DE, Myatt M, Bertagnolio S, Sutherland D, Gilks CF. Recommendations for surveillance of transmitted HIV drug resistance in countries scaling up antiretroviral treatment. Antivir Ther. 2008;13:S25–S36. - PubMed
-
- Berrey MM, Schacker T, Collier AC, Shea T, Brodie SJ, Mayers D, Coombs R, Krieger J, Chun TW, Fauci A, Self SG, Corey L. Treatment of primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection with potent antiretroviral therapy reduces frequency of rapid progression to AIDS. J Infect Dis. 2001;183:1466–1475. - PubMed
-
- Chi BH, Cantrell RA, Zulu I, Mulenga LB, Levy JW, Tambatamba BC, Reid S, Mwango A, Mwinga A, Bulterys M, Saag MS, Stringer JS. Adherence to first-line antiretroviral therapy affects non-virologic outcomes among patients on treatment for more than 12 months in Lusaka, Zambia. Int J Epidemiol. 2009;38:746–756. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chi BH, Mwango A, Giganti M, Mulenga LB, Tambatamba-Chapula B, Reid SE, Bolton-Moore C, Chintu N, Mulenga PL, Stringer EM, Sheneberger R, Mwaba P, Stringer JS. Early clinical and programmatic outcomes with tenofovir-based anti-retroviral therapy in Zambia. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2010;54:63–70. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cohen MS, Chen YQ, McCauley M, Gamble T, Hosseinipour MC, Kumarasamy N, Hakim JG, Kumwenda J, Grinsztejn B, Pilotto JH, Godbole SV, Mehendale S, Chariyalertsak S, Santos BR, Mayer KH, Hoffman IF, Eshleman SH, Piwowar-Manning E, Wang L, Makhema J, Mills LA, de Bruyn G, Sanne I, Eron J, Gallant J, Havlir D, Swindells S, Ribaudo H, Elharrar V, Burns D, Taha TE, Nielsen-Saines K, Celentano D, Essex M, Fleming TR HPTN 052 Study Team. Prevention of HIV-1 infection with early antiretroviral therapy. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:493–505. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

