Pharmacovigilance from social media: mining adverse drug reaction mentions using sequence labeling with word embedding cluster features
- PMID: 25755127
- PMCID: PMC4457113
- DOI: 10.1093/jamia/ocu041
Pharmacovigilance from social media: mining adverse drug reaction mentions using sequence labeling with word embedding cluster features
Abstract
Objective: Social media is becoming increasingly popular as a platform for sharing personal health-related information. This information can be utilized for public health monitoring tasks, particularly for pharmacovigilance, via the use of natural language processing (NLP) techniques. However, the language in social media is highly informal, and user-expressed medical concepts are often nontechnical, descriptive, and challenging to extract. There has been limited progress in addressing these challenges, and thus far, advanced machine learning-based NLP techniques have been underutilized. Our objective is to design a machine learning-based approach to extract mentions of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) from highly informal text in social media.
Methods: We introduce ADRMine, a machine learning-based concept extraction system that uses conditional random fields (CRFs). ADRMine utilizes a variety of features, including a novel feature for modeling words' semantic similarities. The similarities are modeled by clustering words based on unsupervised, pretrained word representation vectors (embeddings) generated from unlabeled user posts in social media using a deep learning technique.
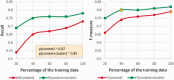
Results: ADRMine outperforms several strong baseline systems in the ADR extraction task by achieving an F-measure of 0.82. Feature analysis demonstrates that the proposed word cluster features significantly improve extraction performance.
Conclusion: It is possible to extract complex medical concepts, with relatively high performance, from informal, user-generated content. Our approach is particularly scalable, suitable for social media mining, as it relies on large volumes of unlabeled data, thus diminishing the need for large, annotated training data sets.
Keywords: ADR; adverse drug reaction; deep learning word embeddings; machine learning; natural language processing; pharmacovigilance; social media mining.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Medical Informatics Association.
Figures





References
-
- Aagaard L, Nielsen LH, Hansen EH. Consumer reporting of adverse drug reactions: a retrospective analysis of the Danish adverse drug reaction database from 2004 to 2006. Drug Saf. 2009;32:1067–1074. - PubMed
-
- Avery AJ, Anderson C, Bond CM, et al. Evaluation of patient reporting of adverse drug reactions to the UK “Yellow Card Scheme”: literature review, descriptive and qualitative analyses, and questionnaire surveys. Southampton: NIHR HTA; 2011. doi:10.3310/hta15200. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

