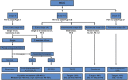
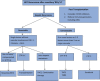
Treatment algorithms for managing hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 25755616
- PMCID: PMC4284287
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2014.05.004
Treatment algorithms for managing hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Early diagnosis and aggressive therapy improves outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Several potentially curative as well as palliative treatment options are available for patients. The choice of therapy is influenced by factors such as extent of tumor and severity of underlying liver dysfunction as well as availability of resources and of expertise. A systematic, algorithmic approach would ensure optimal therapy for each patient and is likely to improve outcomes. Even after receiving therapy for HCC, patients remain at risk for recurrent HCC as well as progression of underlying cirrhosis. Proper assessment and monitoring is needed for the underlying liver disease, which may progress to liver failure and have a major impact on long-term survival. Comprehensive care for patients with cirrhosis includes interventions such as antiviral therapy for HBV and HCV, abstention from alcohol, management of fatty liver disease, endoscopic surveillance and treatment for complications of portal hypertension and, if indicated, immunization against HAV and HBV. An algorithmic approach is useful for choosing the most appropriate treatment option for the individual patient from among the various options that are available. The general consensus is that the BCLC system should be preferred for staging HCC as it is useful in predicting outcomes and planning treatment. The BCLC system classifies patients with HCC into five categories: very early, early, intermediate, advanced, and terminal. It incorporates data on tumor status (number and size of nodules, vascular invasion, extra-hepatic spread), liver function (CTP status, presence of portal hypertension) and overall health status (constitutional symptoms, cancer symptoms, performance status). Treatment allocation according to sub-class of patients is a merit of the BCLC system; a few limitations have been noted, particularly with respect to patients with BCLC stage B and C disease. The treatment algorithm as per BCLC system is summarized in this review.
Keywords: AJCC–UICC, American Joint Committee on Cancer and Union for International Cancer Control; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; BCLC; BCLC, Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer; CEUS, contrast-enhanced ultrasound; CLIP, Cancer of the Liver Italian Program; CTP, Child–Turcotte–Pugh criteria; CUPI, Chinese University Prognostic Index; EASL, European expert panel; EBRT, external beam radiotherapy; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; JIS, Japanese integrated system; LT, liver transplantation; MAA, macro-aggregate albumin; MCT, microwave coagulation therapy; MWA, microwave ablation; NCCN, National Comprehensive Cancer Network; PAI, percutaneous acetic acid injection; PEI, percutaneous ethanol injection; PLT, primary LT; RBV, ribavirin; RECIST, response evaluation criteria in solid tumors; RFA, radiofrequency ablation; SIRT, Selective Internal Radiation Treatment; SLT, salvage liver transplant; TACE, trans-catheter arterial chemo-embolization; TACE-DEB, TACE with drug eluting beads; TAE, transarterial embolization; TAI, trans-catheter hepatic arterial infusion; TARE, transarterial radio-embolization; TNM, Tumor-Node-Metastasis; WHO, World Health Organization; bm-JIS, biomarker JIS; liver cancer; staging; treatment algorithm.
Figures
References
-
- The Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) Investigators A new prognostic system for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study of 435 patients. Hepatology. 1998;28:751–755. - PubMed
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver, European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer EASL–EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012;56:908–943. - PubMed
-
- Okuda K., Ohtsuki T., Obata H. Natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma and prognosis in relation to treatment. Study of 850 patients. Cancer. 1985;56:918–928. - PubMed
-
- Pugh R.N., Murray-Lyon I.M., Dawson J.L., Pietroni M.C., Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973;60:646–649. - PubMed
-
- Edge S.B., Byrd D.R., Compton C.C., editors. AJCC Cancer Staging Handbook. 7th ed. Springer; New York: 2010.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous