Analysis of T-cell epitopes of Der f3 in Dermatophagoides farina
- PMID: 25755700
- PMCID: PMC4348817
Analysis of T-cell epitopes of Der f3 in Dermatophagoides farina
Abstract
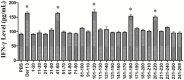
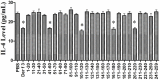
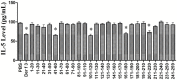
House dust mites (HDM) are most important indoor allergens for humans. Der f3, one of the potent allergens with allergenicity, is derived from Dermatophagoides farina (D. farinae), and exhibits strong allergenicity that was confirmed in our previous work. The current study was undertaken to determine the localization of T-cell epitope of Der f3. We initially developed the T-cell fraction from BALB/c mice sensitized with recombinant Der f3 to determine the T-cell epitopes in the murine models, and performed T cell proliferation assay with 25 synthetic overlapping peptides of Der f3. The results indicated that T-cell reactive region of murine were assigned on amino acid range 41-60, 101-120, 161-180 and 201-220, respectively. In addition, we did T-cell proliferation experiment, respectively using the 4 murine T-cell epitope peptide and the human T-cell lines from three patients allergic to mite allergens in order to verify homogenous T-cell epitopes in humans. The results indicated that the amino acid sequences of 41-60, 101-120 and 161-180 had induced T cell proliferation in humans, yet 201-220 failed to. These findings suggest that T-cell epitope in Der f3 is located in the amino acid sequences of 41-60, 101-120 and 161-180, respectively. T-cell epitope localization detected in our study may provide a basis for development of animal therapeutic model and peptide vaccine for asthma.
Keywords: Allergen; Der f3; T-cell epitope; asthma; house dust mite.
Figures




Similar articles
-
IgE binding activities and in silico epitope prediction of Der f 32 in Dermatophagoides farinae.Immunol Lett. 2019 Sep;213:46-54. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2019.07.006. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Immunol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31381937
-
Quantification of Der f 1 in houses of patients allergic to house dust mite, Dermatophagoides farinae, using a locally produced detection reagents.Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2011 Mar;29(1):78-85. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21560492
-
A hypoallergenic peptide mix containing T cell epitopes of the clinically relevant house dust mite allergens.Allergy. 2019 Dec;74(12):2461-2478. doi: 10.1111/all.13956. Epub 2019 Oct 3. Allergy. 2019. PMID: 31228873 Free PMC article.
-
[Allergens from Dermatophagoides dust mites: origin, antigenic and structural characteristics, and therapeutic agents].Biokhimiia. 1995 Feb;60(2):218-37. Biokhimiia. 1995. PMID: 7718666 Review. Russian.
-
Strategies to query and display allergy-derived epitope data from the immune epitope database.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013;160(4):334-45. doi: 10.1159/000343880. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23172234 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferreira F, Wallner M, Breiteneder H, Hartl A, Thalhamer J, Ebner C. Genetic engineering of allergens: future therapeutic products. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2002;128:171–178. - PubMed
-
- Yasue M, Yokota T, Yuasa M, Kajiwara Y, Suko M, Okudaira H. Effects of oral hyposensitization with recombinant Der f2 on immediate airway constriction in a murine allergic model. Eur Respir J. 1998;11:144–150. - PubMed
-
- Arlian LG. House-dust-mite allergens: a review. Exp Appl Acarol. 1991;10:167–186. - PubMed
-
- Platts-Mills TA, Thomas WR, Aalberse RC, Vervloet D, Champman MD. Dust mite allergens and asthma: report of a second international workshop. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992;89:1046–1060. - PubMed
-
- Arlian LG, Platts-Mills TA. The biology of dust mites and the remediation of mite allergens in allergic disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;107:S406–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
