Decreased expression of TFPI-2 correlated with increased expression of CD133 in cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 25755719
- PMCID: PMC4348830
Decreased expression of TFPI-2 correlated with increased expression of CD133 in cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Recent findings suggest decreasing TFPI-2 expression plays a significant role in inhibiting cell migration and tumor invasion. The clinicopathological significance of the expression of TFPI-2 and its possible correlation with the expression of CD133 in cholangiocarcinoma remains to be solved.
Methods: We investigated if TFPI-2 was involved in the clinicopathological significance of cholangiocarcinoma. An immunohistochemical method was used to detect 218 cases of cholangiocarcinoma, 30 para-neoplastic and 20 normal bile ducts for their expression status of TFPI-2 and CD133, and then the results were analyzed with the patient's age, sex, tumor site and the histological grade, clinical stage as well as overall mean survival time.
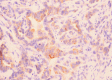
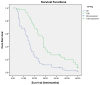
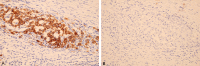
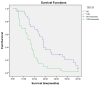
Results: Compared with the para-neoplastic and normal cholangiocytes, the expression of TFPI-2 was obviously decreased while the expression of CD133 in carcinoma cells was increased. Carcinomas with low expression of TFPI-2 were significantly corresponding to the tumor site (P = 0.006), size (P = 0.005), histological grade (P = 0.0001) and clinical stage (P = 0.0001), but not to the age (P = 0.066) and sex (P = 0.411), respectively. By Kaplan-Meier survival analysis, the low expression of TFPI-2 was significantly correlative with the overall survival time (P = 0.0001). Further, the expression of TFPI-2 was found inversely correlative with the expression of CD133 (g = -0.3876, P < 0.0001).
Conclusions: Our finding suggests that the decreased expression of TFPI-2 may play an important role in the carcinogenesis and progression, and may become a new adjunct marker in the diagnosis and prognosis in cholangiocarcinoma. The expression of TFPI-2 may be inversely correlative with the expression of CD133.
Keywords: CD133; Cholangiocarcinoma; TFPI-2; immunohistochemistry; prognosis.
Figures
References
-
- Gores GJ. A spotlight on cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:1536–1538. - PubMed
-
- Heron DE, Stein DE, Eschelman DJ, Topham AK, Waterman FM, Rosato EL, Alden M, Anne PR. Cholangiocarcinoma: the impact of tumor location and treatment strategy on outcome. Am J Clin Oncol. 2003;26:422–428. - PubMed
-
- Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Maitra A, Montes-De-Oca R, Gerstenblith MR, Briggs K, Parker AR, Shimada Y, Eshleman JR, Watkins DN, Beachy PA. Widespread requirement for Hedgehog ligand stimulation in growth of digestive tract tumors. Nature. 2003;425:846–851. - PubMed
-
- Udagawa K, Yasumitsu H, Esaki M, Sawada H, Nagashima Y, Aoki I, Jin M, Miyagi E, Nakazawa T, Hirahara F, Miyazaki K, Miyagi Y. Subcellular localization of PP5/TFPI-2 in human placenta: a possible role of PP5/TFPI-2 as an anti-coagulant on the surface of syncytiotrophoblasts. Placenta. 2002;23:145–153. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
