Epidemiological and pathobiological profiles of Clostridium perfringens infections: review of consecutive series of 33 cases over a 13-year period
- PMID: 25755747
- PMCID: PMC4348875
Epidemiological and pathobiological profiles of Clostridium perfringens infections: review of consecutive series of 33 cases over a 13-year period
Abstract
Background: Although Clostridium perfringens (C. perfringens) is well known as the causative agent of several forms of enteric disease, precise epidemiological and pathobiological aspects are still unknown.
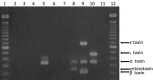
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the culture results of samples collected in our hospital from 2001 through 2013. In addition, for the detection and toxinogenic typing of C. perfringens, polymerase-chain-reaction amplification (PCR)-based rapid analysis was performed in 6 cases using DNA extracted from paraffin-embedded tissues.
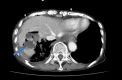
Results: A total of 35 samples from 33 cases were positive for C. perfringens, representing an incidence of 0.017% (35/205, 114). Among 33 patients, 21 patients manifested sepsis and 7 patients had bacteremia. One of the septic cases was complicated by fatal intravascular hemolysis and thus, the prevalence was estimated at 3.0% among C. perfringens infections (1/33). The direct causative disease or state for C. perfringens infection was identified in 18 patients: surgery or intervention for cancers, 8 patients; chemotherapy for cancer, 2 patients; surgery or intervention for non-neoplastic disease, 6 patients; liver cirrhosis, 3 patients, etc. PCR-based toxinogenic typing of C. perfringens detected the alpha-toxin gene only in tissue from a patient who died of massive hemolysis; none of the toxin genes could be amplified in the other 5 cases examined.
Conclusions: The prevalence of overt C. perfringens infection is low, but upon detection, infected patients should be carefully monitored for fatal acute hemolysis caused by type A C. perfringens. Furthermore, PCR-based rapid detection of C. perfringens and toxinogenic typing by archival pathological material is applicable as a diagnostic tool.
Keywords: Clostridium perfringens; alpha-toxin; fatal acute hemolysis; polymerase-chain-reaction amplification.
Figures

References
-
- van Bunderen CC, Bomers MK, Wesdorp E, Peerbooms P, Veenstra J. Clostridium perfringens septicaemia with massive intravascular haemolysis: a case report and review of the literature. Neth J Med. 2010;68:343–346. - PubMed
-
- Petrillo TM, Beck-Sague CM, Songer JG, Abramowsky C, Fortenberry JD, Meacham L, Dean AG, Lee H, Bueschel DM, Nesheim SR. Enteritis necroticans (pigbel) in a diabetic child. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1250–1253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
