Sex-specific association of the SPTY2D1 rs7934205 polymorphism and serum lipid levels
- PMID: 25755761
- PMCID: PMC4348833
Sex-specific association of the SPTY2D1 rs7934205 polymorphism and serum lipid levels
Abstract
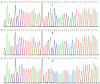
The objective of the present study was to detect the association of the rs7934205 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) near the Suppressor of Ty, domain containing 1 gene (SPTY2D1) and serum lipid levels between males and females in the Mulao and Han populations. Genotyping of SPTY2D1 rs7934205 SNP was performed in 933 of Mulao and 865 of Han participants using polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism. The T allele frequency was different between Mulao males and females (23.2% vs. 27.9%, P = 0.018). The genotype and allele frequencies were also different between Han males and females (P = 0.020 and P = 0.004; respectively). Serum levels of apolipoprotein (Apo) A1 in Mulao males; and total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), ApoA1 and ApoB in Mulao females were different between the CC and CT/TT genotypes (P < 0.05). Serum TC, ApoB levels in Han males, and ApoB levels in Han females were different between the CC and CT/TT genotypes (P < 0.05). The subjects with CT/TT genotype in both Mulao and Han males and females have more favorable lipid profiles than those with CC genotype. These findings suggest that the association between the SPTY2D1 rs7934205 SNP and serum lipid levels might have ethnic- and/or sex-specificity.
Keywords: Lipids; SPTY2D1; environmental factors; sex-specific association; single nucleotide polymorphism.
Figures

References
-
- Yang ZJ, Liu J, Ge JP, Chen L, Zhao ZG, Yang WY China National Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders Study Group. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease risk factor in the Chinese population: the 2007-2008 China National Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders Study. Euro Heart J. 2012;33:213–220. - PubMed
-
- Ginsberg HN, Stalenhoef AF. The metabolic syndrome targeting dyslipidaemia to reduce coronary risk. J Cardiovasc Risk. 2003;10:121–128. - PubMed
-
- Randomised trial of cholesterol lowering. Randomised trial of cholesterol lowering in 4444 patients with coronary heart disease: the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S) Lancet. 1994;344:1383–1389. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
