Elevated Aurora B expression contributes to chemoresistance and poor prognosis in breast cancer
- PMID: 25755770
- PMCID: PMC4348845
Elevated Aurora B expression contributes to chemoresistance and poor prognosis in breast cancer
Abstract
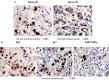
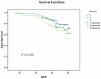
Aurora-B is a major kinase responsible for appropriate mitotic progression. Elevated expression of Aurora-B has been frequently associated with several types of cancer, including breast cancer. However, it is not clear whether the alteration contributes to tumor responses to therapies and prognosis. In this study, we conducted immunohistochemistry using antibodies against Aurora-B, S1981p-ATM, Ki67, and p53 in paraffin-embedded tumor tissues from 312 invasive breast cancer patients. The correlation between disease-free-survival (DFS) and Aurora-B expression was analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test. A Cox proportional hazards regression analysis was used to determine whether Aurora-B was an independent prognostic factor for breast cancer. We found that Aurora-B expression was correlated with the proliferation index (P < 0.001) and p53 expression (P = 0.014) in breast cancer tissues. Further we found that Aurora-B expression was associated with lymph node metastasis (P = 0.002) and histological grade (P = 0.001). Multivariate analyses indicated that elevated Aurora-B expression predicted a poor survival. In a subgroup of patients that received neoadjuvant chemotherapy, we found that elevated Aurora-B contributed to chemoresistance (P = 0.011). In conclusion, elevated Aurora-B expression in breast cancer patients contributes to chemoresistance and predicts poor prognosis.
Keywords: Aurora-B; breast cancer; chemoresistance; prognosis.
Figures
References
-
- Carmena M, Earnshaw WC. The cellular geography of aurora kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:842–54. - PubMed
-
- Gully CP, Velazquez-Torres G, Shin JH, Fuentes-Mattei E, Wang E, Carlock C, Chen J, Rothenberg D, Adams HP, Choi HH, Guma S, Phan L, Chou PC, Su CH, Zhang F, Chen JS, Yang TY, Yeung SC, Lee MH. Aurora B kinase phosphorylates and instigates degradation of p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:E1513–22. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
