Use of Mitomycin C for Refractory Esophageal Stricture following Tracheoesophageal Fistula Repair
- PMID: 25755944
- PMCID: PMC4335951
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0033-1341418
Use of Mitomycin C for Refractory Esophageal Stricture following Tracheoesophageal Fistula Repair
Abstract
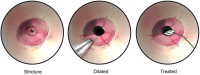
Esophageal stricture is a well-described complication following tracheoesophageal fistula repair. Herein, we report two patients who had persistent esophageal strictures after several months of repeat balloon dilatations. Each patient was treated with a single application of topical mitomycin C in addition to esophageal dilatation, which resulted in complete resolution of the stricture.
Keywords: esophageal stricture; mitomycin C; tracheoesophageal fistula.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Engum S A Grosfeld J L West K W Rescorla F J Scherer L R III Analysis of morbidity and mortality in 227 cases of esophageal atresia and/or tracheoesophageal fistula over two decades Arch Surg 19951305502–508., discussion 508–509 - PubMed
-
- Berger M, Ure B, Lacher M. Mitomycin C in the therapy of recurrent esophageal strictures: hype or hope? Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2012;22(2):109–116. - PubMed
-
- Olutoye O O, Shulman R J, Cotton R T. Mitomycin C in the management of pediatric caustic esophageal strictures: a case report. J Pediatr Surg. 2006;41(5):e1–e3. - PubMed
-
- Kovesi T, Rubin S. Long-term complications of congenital esophageal atresia and/or tracheoesophageal fistula. Chest. 2004;126(3):915–925. - PubMed
-
- Uhlen S, Fayoux P, Vachin F. et al.Mitomycin C: an alternative conservative treatment for refractory esophageal stricture in children? . Endoscopy. 2006;38(4):404–407. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

