Drivers of hospitalization cost after craniotomy for tumor resection: creation and validation of a predictive model
- PMID: 25756732
- PMCID: PMC4351828
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-015-0742-2
Drivers of hospitalization cost after craniotomy for tumor resection: creation and validation of a predictive model
Abstract
Background: The economic sustainability of all areas of medicine is under scrutiny. Limited data exist on the drivers of cost after a craniotomy for tumor resection (CTR). The objective of the present study was to develop and validate a predictive model of hospitalization cost after CTR.
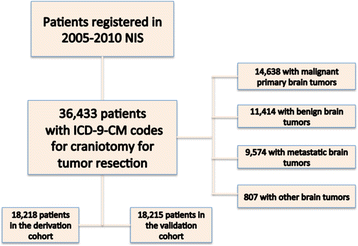
Methods: We performed a retrospective study involving CTR patients who were registered in the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS) database from 2005-2010. This cohort underwent 1:1 randomization to create derivation and validation subsamples. Regression techniques were used for the creation of a parsimonious predictive model.
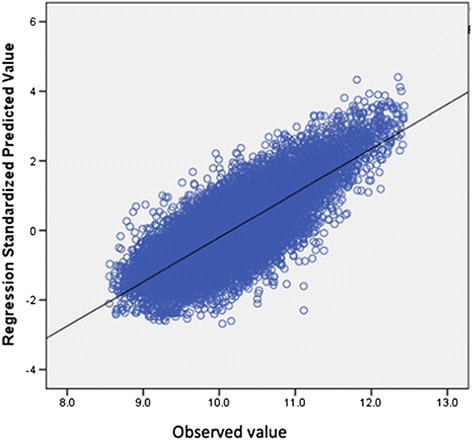
Results: Of the 36,433 patients undergoing CTR, 14638 (40.2%) underwent craniotomies for primary malignant, 9574 (26.3%) for metastatic, and 11414 (31.3%) for benign tumors. The median hospitalization cost was $24,504 (Interquartile Range (IQR), $4,265-$44,743). Common drivers of cost identified in the multivariate analyses included: length of stay, number of procedures, hospital size and region, and patient income. The models were validated in independent cohorts and demonstrated final R2 very similar to the initial models. The predicted and observed values in the validation cohort demonstrated good correlation.
Conclusions: This national study identified significant drivers of hospitalization cost after CTR. The presented model can be utilized as an adjunct in the cost containment debate and the creation of data-driven policies.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical