Efficacy and safety of fixed-dose combinations of aclidinium bromide/formoterol fumarate: the 24-week, randomized, placebo-controlled AUGMENT COPD study
- PMID: 25756831
- PMCID: PMC4213545
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-014-0123-0
Efficacy and safety of fixed-dose combinations of aclidinium bromide/formoterol fumarate: the 24-week, randomized, placebo-controlled AUGMENT COPD study
Abstract
Background: Combining two long-acting bronchodilators with complementary mechanisms of action may provide treatment benefits to patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) that are greater than those derived from either treatment alone. The efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose combination (FDC) of aclidinium bromide, a long-acting muscarinic antagonist, and formoterol fumarate, a long-acting β2-agonist, in patients with moderate to severe COPD are presented.
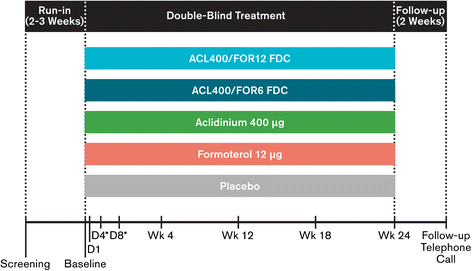
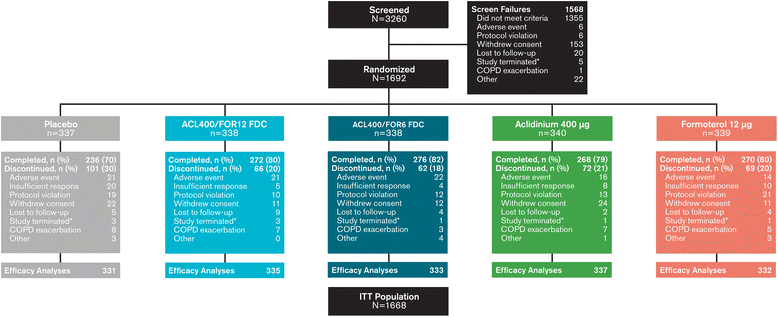
Methods: In this 24-week double-blind study, 1692 patients with stable COPD were equally randomized to twice-daily treatment with FDC aclidinium 400 μg/formoterol 12 μg (ACL400/FOR12 FDC), FDC aclidinium 400 μg/formoterol 6 μg (ACL400/FOR6 FDC), aclidinium 400 μg, formoterol 12 μg, or placebo administered by a multidose dry powder inhaler (Genuair®/Pressair®)*. Coprimary endpoints were change from baseline to week 24 in 1-hour morning postdose FEV1 (FDCs versus aclidinium) and change from baseline to week 24 in morning predose (trough) FEV1 (FDCs versus formoterol). Secondary endpoints were change from baseline in St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) total score and improvement in Transition Dyspnea Index (TDI) focal score at week 24. Safety and tolerability were also assessed.
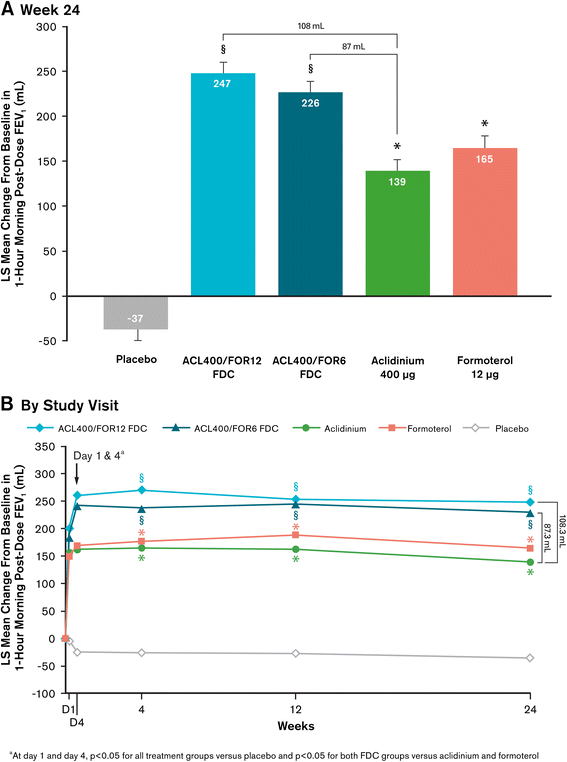
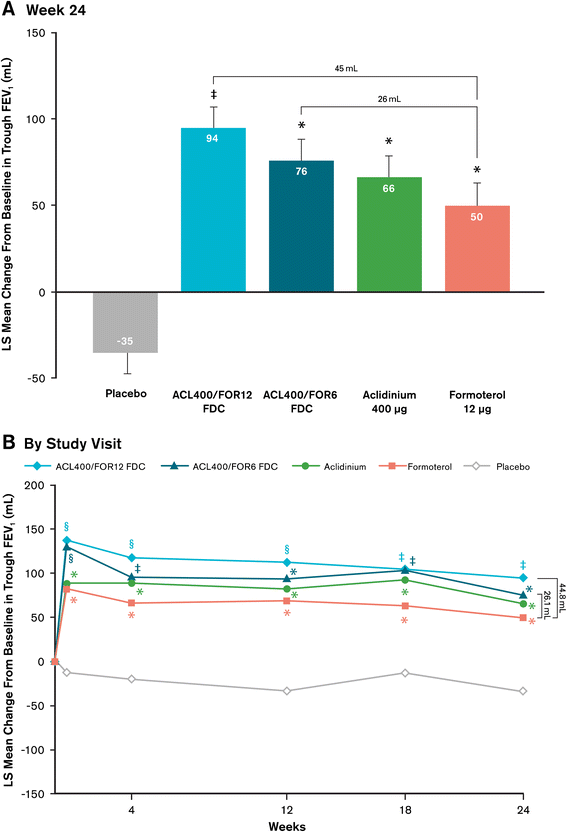
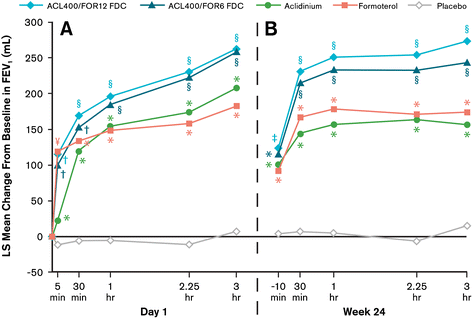
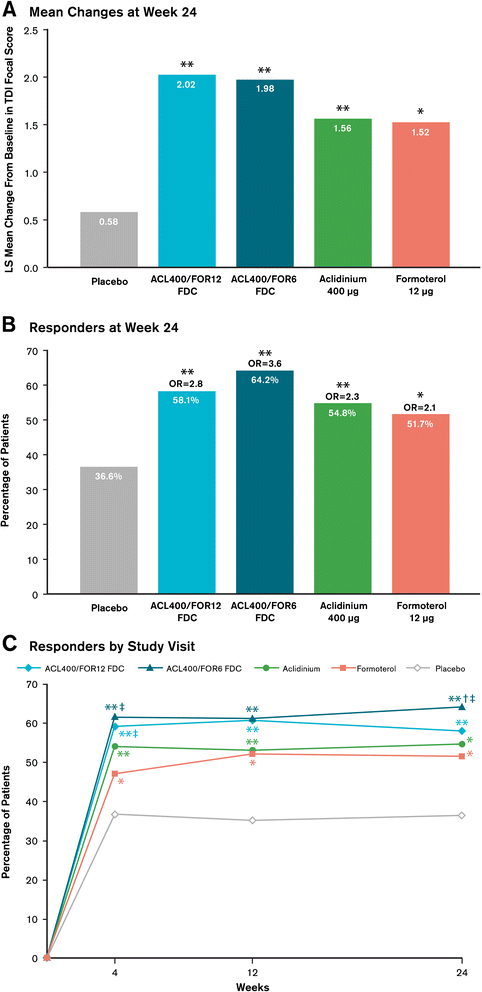
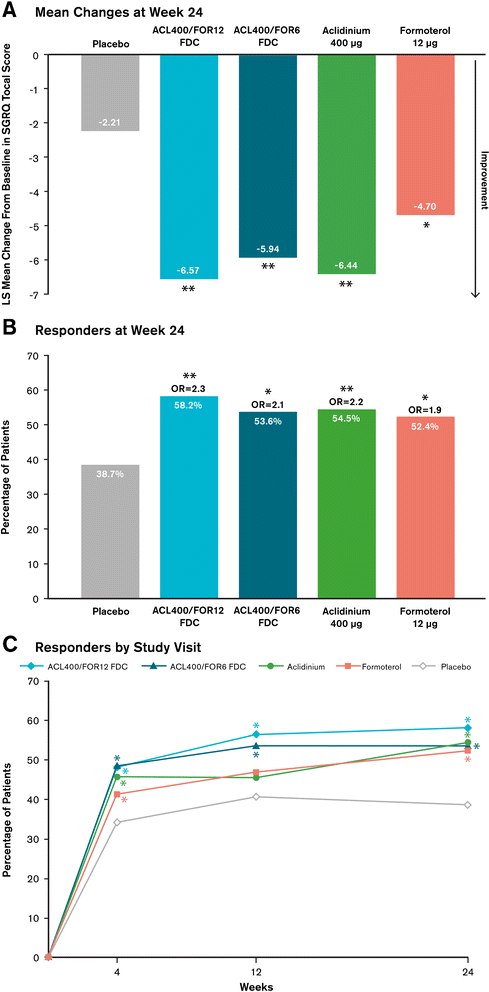
Results: At study end, improvements from baseline in 1-hour postdose FEV1 were significantly greater in patients treated with ACL400/FOR12 FDC or ACL400/FOR6 FDC compared with aclidinium (108 mL and 87 mL, respectively; p < 0.0001). Improvements in trough FEV1 were significantly greater in patients treated with ACL400/FOR12 FDC versus formoterol (45 mL; p = 0.0102), a numerical improvement of 26 mL in trough FEV1 over formoterol was observed with ACL400/FOR6 FDC. Significant improvements in both SGRQ total and TDI focal scores were observed in the ACL400/FOR12 FDC group at study end (p < 0.0001), with differences over placebo exceeding the minimal clinically important difference of ≥4 points and ≥1 unit, respectively. All treatments were well tolerated, with safety profiles of the FDCs similar to those of the monotherapies.
Conclusions: Treatment with twice-daily aclidinium 400 μg/formoterol 12 μg FDC provided rapid and sustained bronchodilation that was greater than either monotherapy; clinically significant improvements in dyspnea and health status were evident compared with placebo. Aclidinium/formoterol FDC may be an effective and well tolerated new treatment option for patients with COPD.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov NCT01437397.
Figures
References
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD): Global strategy for the diagnosis, management and prevention of COPD (2014 update). [http://www.goldcopd.org/]
-
- Mahler DA, D'Urzo A, Bateman ED, Ozkan SA, White T, Peckitt C, Lassen C, Kramer B, Intrust study investigators Concurrent use of indacaterol plus tiotropium in patients with COPD provides superior bronchodilation compared with tiotropium alone: a randomised, double-blind comparison. Thorax. 2012;67:781–788. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2011-201140. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

