microRNA-18b modulates insulin-like growth factor-1 expression in deer antler cell proliferation by directly targeting its 3' untranslated region
- PMID: 25756952
- PMCID: PMC4390164
- DOI: 10.1089/dna.2014.2421
microRNA-18b modulates insulin-like growth factor-1 expression in deer antler cell proliferation by directly targeting its 3' untranslated region
Abstract
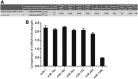
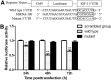
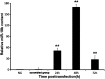
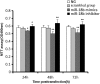
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) is a multipromoter gene that has complex biological functions and plays an important role in Chinese sika deer antler cell differentiation and proliferation. microRNAs and their roles in deer antler growth have attracted much attention. In the present study, to investigate the effect of microRNAs on the regulation of IGF-1 during the rapid growth of antlers, miRNA GeneChip analysis and TargetScan Human software were used to screen microRNAs that bind to the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of IGF-1. The results indicated that a significantly differential expression of miR-18b was observed in cartilage and mesenchymal of antler tip tissue and the presence of miR-18b-binding sites within the IGF-1 3'UTR. A miR-18b mimic was then transfected into antler cartilage cells to overexpress miR-18b and the expression levels were quantified by real-time PCR. Real-time PCR showed that the expression level of miR-18b in transfected cells was significantly increased compared with the control group (p<0.01). Dual luciferase assays revealed that miR-18b decreased the fluorescence value of the luciferase reporter gene in the group transfected with the wild-type vector of IGF-1 3'UTR. In contrast, the relative luciferase activity in the group transfected with the mutant vector of IGF-1 3'UTR did not change obviously. MTT assays and cell cycle analyses confirmed that overexpression of the miR-18b mimic inhibited the proliferation of cartilage cells. In contrast, transfection of a miR-18b inhibitor increased the cell proliferation rate. Furthermore, Western blot analyses revealed that overexpression of miR-18b mimics downregulated the protein levels of IGF-1, while IGF-1 expression increased after transfection of miR-18b inhibitors. Taken together, our findings show that miR-18b is a potentially novel target in deer antler cell proliferation. miR-18b may modulate IGF-1 expression of sika deer antler.
Figures

References
-
- Ambros V. (2004). The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431,350–355 - PubMed
-
- Bartel D.P. (2004). MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116,281–297 - PubMed
-
- Francis S.M., and Suttie J.M. (1998). Detection of growth factors and proto-oncogene mRNA in the growing tip of red deer (Cervus elaphus) antler using reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). J Exp Zool 281,36–42 - PubMed
-
- Gu L., Mo E., Yang Z., Zhu X., Fang Z., Sun B., Wang C., Bao J., and Sung C. (2007). Expression and localization of insulin-like growth factor-I in four parts of the red deer antler. Growth Factors 25,264–279 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

