Proximal Roux-en-Y gastric bypass alters drug absorption pattern but not systemic exposure of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein substrates
- PMID: 25757445
- PMCID: PMC4696861
- DOI: 10.1002/phar.1560
Proximal Roux-en-Y gastric bypass alters drug absorption pattern but not systemic exposure of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein substrates
Abstract
Study objectives: To evaluate the effect of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery (RYGB) on the pharmacokinetics of midazolam (a CYP3A4 substrate) and digoxin (a P-glycoprotein substrate).
Design: Prospective, nonblinded, longitudinal, single-dose pharmacokinetic study in three phases: presurgery baseline and postoperative assessments at 3 and 12 months.
Patients: Twelve obese patients meeting current standards for bariatric surgery.
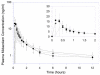
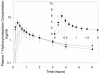
Measurements and main results: At each study visit, patients received a single dose of oral digoxin and midazolam at 8 a.m. Blood samples were collected at regular intervals for 24 hours after dosing. Continuous 12-lead electrocardiogram (EKG), heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate were monitored, and pharmacokinetic parameters from the three visits were compared. The peak plasma concentration (Cmax ) of midazolam increased by 66% and 71% at 3- and 12-month post-RYGB (p=0.017 and p=0.001, respectively), whereas the median time to peak concentration (Tmax ) was reduced by 50%. The mean Cmax for 1'-hydroxymidazolam increased by 87% and 80% at 3 and 12 months (p=0.001 and p<0.001, respectively). However, neither the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) for midazolam nor the metabolite-to-parent AUC ratio changed significantly over time. For digoxin, the median Tmax decreased from 40 minutes at baseline to 30 and 20 minutes at 3 and 12 months, respectively. The mean AUC for digoxin, heart rate, and EKG patterns were similar across the three study phases.
Conclusion: Contemporary proximal RYGB increases the rate of drug absorption without significantly changing the overall exposure to midazolam and digoxin. The Cmax of a CYP3A4 substrate with a high extraction ratio was substantially increased after RYGB.
Keywords: CYP3A4; P-glycoprotein; Roux-en-Y gastric bypass; absorption; bariatric surgery; obesity; pharmacokinetics.
© 2015 Pharmacotherapy Publications, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Hallersund P, Sjöström L, Olbers T, et al. Gastric bypass surgery is followed by lowered blood pressure and increased diuresis—long term results from the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) study. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e49696. Erratum in: PLoS One. 2013;8. doi:10.1371/annotation/88dbb5b7-3f7e-4b26- a5b6-f020d33f0182. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carlsson LM, Peltonen M, Ahlin S, et al. Bariatric surgery and prevention of type 2 diabetes in Swedish obese subjects. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:695–704. - PubMed
-
- How many bariatric surgeries are taking place? Available from http://www.amednews.com/assets/pdf/2012gbisa0423b.pdf. Accessed October 08, 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

