Cognitive constraints on motor imagery
- PMID: 25758054
- PMCID: PMC4629411
- DOI: 10.1007/s00426-015-0656-y
Cognitive constraints on motor imagery
Abstract
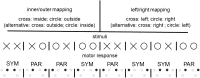
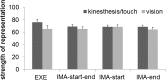
Executed bimanual movements are prepared slower when moving to symbolically different than when moving to symbolically same targets and when targets are mapped to target locations in a left/right fashion than when they are mapped in an inner/outer fashion [Weigelt et al. (Psychol Res 71:238-447, 2007)]. We investigated whether these cognitive bimanual coordination constraints are observable in motor imagery. Participants performed fast bimanual reaching movements from start to target buttons. Symbolic target similarity and mapping were manipulated. Participants performed four action conditions: one execution and three imagination conditions. In the latter they indicated starting, ending, or starting and ending of the movement. We measured movement preparation (RT), movement execution (MT) and the combined duration of movement preparation and execution (RTMT). In all action conditions RTs and MTs were longer in movements towards different targets than in movements towards same targets. Further, RTMTs were longer when targets were mapped to target locations in a left/right fashion than when they were mapped in an inner/outer fashion, again in all action conditions. RTMTs in imagination and execution were similar, apart from the imagination condition in which participants indicated the start and the end of the movement. Here MTs, but not RTs, were longer than in the execution condition. In conclusion, cognitive coordination constraints are present in the motor imagery of fast (<1600 ms) bimanual movements. Further, alternations between inhibition and execution may prolong the duration of motor imagery.
Figures



References
-
- Barr K, Hall C. The use of imagery by rowers. International Journal of Sport Psychology. 1992;23:243–261.
-
- Beilock SL, Carr TH, MacMahon C, Starkes JL. When paying attention becomes counterproductive: impact of divided versus skill-focused attention on novice and experienced performance of sensorimotor skills. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied. 2002;8:6–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

