A rapid interleukin-6 bedside test for the identification of intra-amniotic inflammation in preterm labor with intact membranes
- PMID: 25758618
- PMCID: PMC4776723
- DOI: 10.3109/14767058.2015.1006620
A rapid interleukin-6 bedside test for the identification of intra-amniotic inflammation in preterm labor with intact membranes
Abstract
Objective: Preterm birth is associated with 5-18% of pregnancies and is the leading cause of neonatal morbidity and mortality. Amniotic fluid (AF) interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a key cytokine for the identification of intra-amniotic inflammation, and patients with an elevated AF IL-6 are at risk for impending preterm delivery. However, results of the conventional method of measurement (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; ELISA) are usually not available in time to inform care. The objective of this study was to determine whether a point of care (POC) test or lateral-flow-based immunoassay for measurement of AF IL-6 concentrations can identify patients with intra-amniotic inflammation and/or infection and those destined to deliver spontaneously before term among women with preterm labor and intact membranes.
Methods: One-hundred thirty-six women with singleton pregnancies who presented with symptoms of preterm labor and underwent amniocentesis were included in this study. Amniocentesis was performed at the time of diagnosis of preterm labor. AF Gram stain and AF white blood cell counts were determined. Microbial invasion of the amniotic cavity (MIAC) was defined according to the results of AF culture (aerobic and anaerobic as well as genital mycoplasmas). AF IL-6 concentrations were determined by both lateral flow-based immunoassay and ELISA. The primary outcome was intra-amniotic inflammation, defined as AF ELISA IL-6 ≥ 2600 pg/ml.
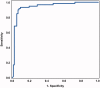
Results: (1) AF IL-6 concentrations determined by a POC test have high sensitivity (93%), specificity (91%) and a positive likelihood ratio of 10 for the identification of intra-amniotic inflammation by using a threshold of 745 pg/ml; (2) the POC test and ELISA for IL-6 perform similarly in the identification of MIAC, acute inflammatory lesions of placenta and patients at risk of impending spontaneous preterm delivery.
Conclusion: A POC AF IL-6 test can identify intra-amniotic inflammation in women who present with preterm labor and intact membranes and those who will subsequently deliver spontaneously before 34 weeks of gestation. Results can be available within 20 min - this has important clinical implications and opens avenues for early diagnosis as well as treatment of intra-amniotic inflammation/infection.
Keywords: Acute chorioamnionitis; ELISA; acute funisitis; biomarkers; microbial invasion of the amniotic cavity; point of care test; prematurity; preterm birth.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
