The impact of two semiannual treatments with albendazole alone on lymphatic filariasis and soil-transmitted helminth infections: a community-based study in the Republic of Congo
- PMID: 25758650
- PMCID: PMC4426585
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.14-0661
The impact of two semiannual treatments with albendazole alone on lymphatic filariasis and soil-transmitted helminth infections: a community-based study in the Republic of Congo
Abstract
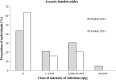
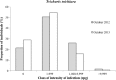
Implementation of mass drug administration (MDA) with ivermectin plus albendazole (ALB) for lymphatic filariasis (LF) has been delayed in central Africa because of the risk of serious adverse events in subjects with high Loa loa microfilaremia. We conducted a community trial to assess the impact of semiannual MDA with ALB (400 mg) alone on LF and soil-transmitted helminth (STH) infections in the Republic of Congo. Evaluation at 12 months showed that ALB MDA had not significantly reduced Wuchereria bancrofti antigenemia or microfilaria (mf) rates in the community (from 17.3% to 16.6% and from 5.3% to 4.2%, respectively). However, the geometric mean mf count in mf-positive subjects was reduced from 202.2 to 80.9 mf/mL (60% reduction, P = 0.01). The effect of ALB was impressive in 38 subjects who were mf-positive at baseline and retested at 12 months: 37% had total mf clearance, and individual mf densities were reduced by 73.0%. MDA also dramatically reduced the hookworm infection rate in the community from 6.5% to 0.6% (91% reduction), with less impressive effects on Ascaris and Trichuris. These preliminary results suggest that semiannual community MDA with ALB is a promising strategy for controlling LF and STH in areas with coendemic loiasis.
© The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . Malaria and Integrated Vector Management; Accra, Ghana: 2012. Provisional strategy for interrupting lymphatic filariasis transmission in loiasis-endemic countries. Proceedings of the Meeting on Lymphatic Filariasis. March 5–9, 2012.
-
- Carme B, Ebikili B, Mbitsi A, Copin N. Essai thérapeutique de l'ivermectine au cours de la loase à moyenne et forte microfilarémie. Ann Soc Belg Med Trop. 1991;71:47–50. - PubMed
-
- Gardon J, Gardon-Wendel N, Demanga-Ngangue, Kamgno J, Chippaux JP, Boussinesq M. Serious reactions after mass treatment of onchocerciasis with ivermectin in an area endemic for Loa loa infection. Lancet. 1997;350:18–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

