Phase 2 trial of dasatinib in target-selected patients with recurrent glioblastoma (RTOG 0627)
- PMID: 25758746
- PMCID: PMC5762006
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nov011
Phase 2 trial of dasatinib in target-selected patients with recurrent glioblastoma (RTOG 0627)
Abstract
Background: We conducted a phase II trial to evaluate the efficacy of dasatinib, a multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, for adults with recurrent glioblastoma (GBM).
Methods: Eligibility requirements were Karnofsky performance status ≥ 60%; no concurrent hepatic enzyme-inducing anticonvulsants; prior treatment with surgery, radiotherapy, and temozolomide exclusively; and activation or overexpression of ≥ 2 putative dasatinib targets in GBM (ie, SRC, c-KIT, EPHA2, and PDGFR). Using a 2-stage design, 77 eligible participants (27 in stage 1, if favorable, and then 50 in stage 2) were needed to detect an absolute improvement in the proportion of patients either alive and progression-free patients at 6 months (6mPFS) or responding (any duration) from a historical 11% to 25%.
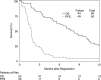
Results: A high rate of ineligibility (27%) to stage 1 precluded a powered assessment of efficacy, but there was also infrequent treatment-related toxicity at 100 mg twice daily. Therefore, the study was redesigned to allow intrapatient escalation by 50 mg daily every cycle as tolerated (stage 1B) before determining whether to proceed to stage 2. Escalation was tolerable in 10 of 17 (59%) participants evaluable for that endpoint; however, among all eligible patients (stages 1 and 1B, n = 50), there were no radiographic responses, median overall survival was 7.9 months, median PFS was 1.7 months, and the 6mPFS rate was 6%. The clinical benefit was insufficient to correlate tested biomarkers with efficacy. The trial was closed without proceeding to stage 2.
Conclusions: Intraparticipant dose escalation was feasible, but dasatinib was ineffective in recurrent GBM. Clinical trials.gov identified. NCT00423735 (available at http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00423735).
Keywords: chemotherapy; dasatinib; glioblastoma; phase II; tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Comment in
-
Dasatinib in recurrent glioblastoma: failure as a teacher.Neuro Oncol. 2015 Jul;17(7):910-1. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nov086. Epub 2015 May 10. Neuro Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25964312 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Brandes AA, Tosoni A, Amista P, et al. How effective is BCNU in recurrent glioblastoma in the modern era? A phase II trial. Neurology. 2004;63(7):1281–1284. - PubMed
-
- Wong ET, Hess KR, Gleason MJ, et al. Outcomes and prognostic factors in recurrent glioma patients enrolled onto phase II clinical trials. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17(8):2572–2578. - PubMed
-
- Friedman HS, Prados MD, Wen PY, et al. Bevacizumab alone and in combination with irinotecan in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(28):4733–4740. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous