MTBP inhibits migration and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 25759210
- PMCID: PMC4510982
- DOI: 10.1007/s10585-015-9706-5
MTBP inhibits migration and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
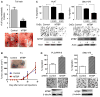
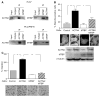
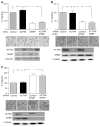
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common cancers worldwide with increasing incidence. Despite curative surgical resection and advanced chemotherapy, its survival rate remains low. The presence of microvascular invasion and occult metastasis is one of the major causes for this poor outcome. MDM2 Binding Protein (MTBP) has been implicated in the suppression of cell migration and cancer metastasis. However, clinical significance of MTBP, particularly in human cancer, is poorly understood. Specifically, clinical relevance of MTBP in human HCC has never been investigated. Here we demonstrated that expression of MTBP was significantly reduced in human HCC tissues compared to adjacent non-tumor tissues. MTBP expression was negatively correlated with capsular/vascular invasion and lymph node metastasis. Overexpression of MTBP resulted in the suppression of the migratory and metastatic potential of HCC cells, while its downregulation increased the migration. Consistent with the previous report, MTBP endogenously bound to alpha-actinin 4 (ACTN4) and suppressed ACTN4-mediated cell migration in multiple HCC cell lines. However, MTBP also inhibited migratory potential of PLC/PRF/5 HCC cells whose migration was not altered by manipulation of ACTN4 expression. These results suggest that mechanisms behind MTBP-mediated migration suppression may not be limited to the pathway involving ACTN4 in certain cellular contexts. Additionally, as a potential mechanism for reduced MTBP expression in tumors, we found that MTBP expression was increased following the treatment with histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDIs). Our study, for the first time, provides clinical relevance of MTBP in the suppression of HCC metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Chen X, Xu Z, Wang Y. Recent advances in breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1. Int J Biol Markers. 2011;26(1):1–8. - PubMed
-
- Guillot C, Hall J, Herceg Z, Merle P, Chemin I. Update on hepatocellular carcinoma breakthroughs: poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors as a promising therapeutic strategy. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2014;38(2):137–142. - PubMed
-
- Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379(9822):1245–1255. - PubMed
-
- Chun JM, Kwon HJ, Sohn J, Kim SG, Park JY, Bae HI, Yun YK, Hwang YJ. Prognostic factors after early recurrence in patients who underwent curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2011;103(2):148–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

