Phosphorylation of eIF2α triggered by mTORC1 inhibition and PP6C activation is required for autophagy and is aberrant in PP6C-mutated melanoma
- PMID: 25759478
- PMCID: PMC4580977
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.aaa0899
Phosphorylation of eIF2α triggered by mTORC1 inhibition and PP6C activation is required for autophagy and is aberrant in PP6C-mutated melanoma
Abstract
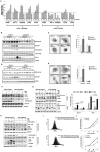
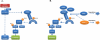
Amino acid deprivation promotes the inhibition of the kinase complex mTORC1 (mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1) and activation of the kinase GCN2 (general control nonrepressed 2). Signaling pathways downstream of both kinases have been thought to independently induce autophagy. We showed that these two amino acid-sensing systems are linked. We showed that pharmacological inhibition of mTORC1 led to activation of GCN2 and phosphorylation of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2α (eIF2α) in a mechanism dependent on the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 6 (PP6C). Autophagy induced by pharmacological inhibition of mTORC1 required PP6C, GCN2, and eIF2α phosphorylation. Although some of the PP6C mutants found in melanoma did not form a strong complex with PP6 regulatory subunits and were rapidly degraded, these mutants paradoxically stabilized PP6C encoded by the wild-type allele and increased eIF2α phosphorylation. Furthermore, these PP6C mutations were associated with increased autophagy in vitro and in human melanoma samples. Thus, these data showed that GCN2 activation and phosphorylation of eIF2α in response to mTORC1 inhibition are necessary for autophagy. Additionally, we described a role for PP6C in this process and provided a mechanism for PP6C mutations associated with melanoma.
Copyright © 2015, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
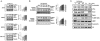



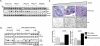
Similar articles
-
Cellular adaptation to nutrient deprivation: crosstalk between the mTORC1 and eIF2α signaling pathways and implications for autophagy.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(16):2571-7. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1056947. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 26039820 Free PMC article.
-
GCN2 contributes to mTORC1 inhibition by leucine deprivation through an ATF4 independent mechanism.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 14;6:27698. doi: 10.1038/srep27698. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27297692 Free PMC article.
-
Fission yeast TORC1 prevents eIF2α phosphorylation in response to nitrogen and amino acids via Gcn2 kinase.J Cell Sci. 2012 Dec 15;125(Pt 24):5955-9. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105395. Epub 2012 Oct 29. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 23108671
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin and tuberous sclerosis complex.J Dermatol Sci. 2015 Aug;79(2):93-100. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2015.04.005. Epub 2015 Apr 25. J Dermatol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26051878 Review.
-
How phosphoinositide 3-phosphate controls growth downstream of amino acids and autophagy downstream of amino acid withdrawal.Biochem Soc Trans. 2012 Feb;40(1):37-43. doi: 10.1042/BST20110684. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012. PMID: 22260663 Review.
Cited by
-
Adaptation of HepG2 cells to a steady-state reduction in the content of protein phosphatase 6 (PP6) catalytic subunit.Exp Cell Res. 2015 Jul 15;335(2):224-37. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.05.008. Epub 2015 May 18. Exp Cell Res. 2015. PMID: 25999147 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Pathways in Melanomagenesis: What We Learned from Next-Generation Sequencing Approaches.Curr Oncol Rep. 2018 Sep 14;20(11):86. doi: 10.1007/s11912-018-0733-7. Curr Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30218391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of GCN2 Reveals Synergy with Cell-Cycle Regulation and Proteostasis.Metabolites. 2023 Oct 9;13(10):1064. doi: 10.3390/metabo13101064. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37887389 Free PMC article.
-
HRI-mediated translational repression reduces proteotoxicity and sensitivity to bortezomib in human pancreatic cancer cells.Oncogene. 2018 Aug;37(32):4413-4427. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0227-y. Epub 2018 May 3. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29720726 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Analysis Identifies p62/SQSTM1 as a Critical Player in PARP Inhibitor Resistance.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 29;12:908603. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.908603. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35847859 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harding HP, Zhang Y, Zeng H, Novoa I, Lu PD, Calfon M, Sadri N, Yun C, Popko B, Paules R, Stojdl DF, Bell JC, Hettmann T, Leiden JM, Ron D. An integrated stress response regulates amino acid metabolism and resistance to oxidative stress. Mol Cell. 2003;11:619–633. - PubMed
-
- Rzymski T, Milani M, Pike L, Buffa F, Mellor HR, Winchester L, Pires I, Hammond E, Ragoussis I, Harris AL. Regulation of autophagy by ATF4 in response to severe hypoxia. Oncogene. 2010;29:4424–4435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

