Nrf2-mediated mucoprotective and anti-inflammatory actions of Artemisia extracts led to attenuate stress related mucosal damages
- PMID: 25759519
- PMCID: PMC4345182
- DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.14-76
Nrf2-mediated mucoprotective and anti-inflammatory actions of Artemisia extracts led to attenuate stress related mucosal damages
Abstract
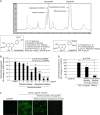
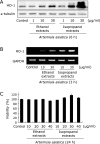
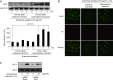
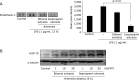
The aim of this study was to compare biological actions between isopropanol and ethanol extracts of Artemisia including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cytoprotective actions. Antioxidant activities were evaluated using 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) method and confocal microscopy on lipopolysaccharide-induced RGM1 cells, cytoprotection effects evaluated by detecting heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), Nf-E2 related factor2 (Nrf2) and heat shock protein 70 (HSP70), and anti-inflammatory effects investigated by measuring inflammatory mediators. Water immersion restraint stress was imposed to provoke stress related mucosal damages (SRMD) in rats. Isopropanol extracts of Artemisia showed the higher DPPH radical scavenging activity and lesser LPS-induced reactive oxygen species productions and increased HO-1 expression through increased nuclear translocation of Nrf2 transcription factor compared to ethanol extracts. The increased expression of HSP70 and decreased expression of endothelin-1 were only increased with isopropanol extracts. A concentration-dependent inhibition of LPS-induced COX-2 and iNOS even at a rather lower concentration than ethanol extract was achieved with isopropanol extracts. Cytokine protein array revealed Artemisia extracts significantly attenuated the levels of CXCL-1, CXCL-16, and MCP-1. These orchestrated actions led to significant rescue from SRMD. Conclusively, Artemisia extracts imposed significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity against SRMD and isopropanol extracts were superior to ethanol extracts in these beneficiary actions of Artemisia.
Keywords: HO-1; anti-inflammation; artemisia asiatica; isopropanol extracts; stress related mucosal damages.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Artemisia asiatica extracts protect against ethanol-induced injury in gastric mucosa of rats.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008 Jun;23(6):976-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05333.x. Epub 2008 Apr 28. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. PMID: 18444990
-
Anti-inflammatory activities and mechanisms of Artemisia asiatica ethanol extract.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Mar 28;152(3):487-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.01.030. Epub 2014 Feb 4. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24503036
-
Combined Extracts of Artemisia and Green Tea, Mitigated Alcoholic Gastritis Via Enhanced Heat-shock Protein 27.Korean J Gastroenterol. 2018 Mar 25;71(3):132-142. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2018.71.3.132. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29566474
-
The protective effect of eupatilin on indomethacin-induced cell damage in cultured feline ileal smooth muscle cells: involvement of HO-1 and ERK.J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Jun 19;118(1):94-101. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2008.03.010. Epub 2008 Mar 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18440740
-
Neuroprotective and anti-epileptic potentials of genus Artemisia L.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 19;13:1021501. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1021501. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36339595 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protective Effect of Artemisia argyi and Its Flavonoid Constituents against Contrast-Induced Cytotoxicity by Iodixanol in LLC-PK1 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 7;19(5):1387. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051387. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29735908 Free PMC article.
-
Eupatilin exerts neuroprotective effects in mice with transient focal cerebral ischemia by reducing microglial activation.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 8;12(2):e0171479. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171479. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28178289 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the Regulatory Effect of Water Extract of Artemisia annua L. on Antioxidant Function of Mutton Sheep via the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jul 18;14(7):885. doi: 10.3390/antiox14070885. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722989 Free PMC article.
-
DCAF12 and HSPA1A May Serve as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Myasthenia Gravis.Biomed Res Int. 2022 May 24;2022:8587273. doi: 10.1155/2022/8587273. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35655486 Free PMC article.
-
Dolichos lablab L. extracts as pharmanutrient for stress-related mucosal disease in rat stomach.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2020 Jul;67(1):89-101. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.20-11. Epub 2020 Jun 11. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32801474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seo HJ, Park KK, Han SS, et al. Inhibitory effects of the standardized extract (DA-9601) of Artemisia asiatica Nakai on phorbol ester-induced ornithine decarboxylase activity, papilloma formation, cyclooxygenase-2 expression, inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and nuclear transcription factor kappa B activation in mouse skin. Int J Cancer. 2002;100:456–462. - PubMed
-
- Lee S, Park HH, Son HY, et al. DA-9601 inhibits activation of the human mast cell line HMC-1 through inhibition of NF-kappaB. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2007;23:105–112. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

