Contrast Volume/Raw eGFR Ratio for Predicting Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention for Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 25759701
- PMCID: PMC4327327
- DOI: 10.1159/000369940
Contrast Volume/Raw eGFR Ratio for Predicting Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention for Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
Background: Considering that contrast medium is excreted through the whole kidney in a similar manner to drug excretion, the use of raw estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) rather than body surface area (BSA)-normalized eGFR is thought to be more appropriate for evaluating the risk of contrast-induced acute kidney injury (CI-AKI).
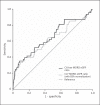
Methods: This study included 2,189 myocardial infarction patients treated with percutaneous coronary intervention. Logistic regression analysis was performed to identify the independent risk factors. We used receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves to compare the ratios of contrast volume (CV) to eGFR with and without BSA normalization in predicting CI-AKI.
Results: The area under the curve (AUC) of the ROC curve for the model including all the significant variables such as diabetes mellitus, left ventricular ejection fraction, preprocedural glucose, and the CV/raw modification of diet in renal disease (MDRD) eGFR ratio was 0.768 [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.720-0.816; p < 0.001]. When the CV/raw MDRD eGFR ratio was used as a single risk value, the AUC of the ROC curve was 0.650 (95% CI, 0.590-0.711; p < 0.001). When the CV/MDRD eGFR ratio with BSA normalization ratio was used, the AUC of the ROC curve further decreased to 0.635 (95% CI, 0.574-0.696; p < 0.001). The difference between the two AUCs was significant (p = 0.002).
Conclusions: Raw eGFR is a better predictor for CI-AKI than BSA-normalized eGFR.
Keywords: Body surface area normalization; Contrast-induced acute kidney injury; Estimated glomerular filtration rate.
Figures

References
-
- Laskey WK, Jenkins C, Selzer F, Marroquin OC, Wilensky RL, Glaser R, Cohen HA, Holmes DR., Jr Volume-to-creatinine clearance ratio: a pharmacokinetically based risk factor for prediction of early creatinine increase after percutaneous coronary intervention. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50:584–590. - PubMed
-
- Nyman U, Bjork J, Aspelin P, Marenzi G. Contrast medium dose-to-GFR ratio: a measure of systemic exposure to predict contrast-induced nephropathy after percutaneous coronary intervention. Acta Radiol. 2008;49:658–667. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Tan N, Zhou YL, He PC, Luo JF, Chen JY. The contrast medium volume to estimated glomerular filtration rate ratio as a predictor of contrast-induced nephropathy after primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Int Urol Nephrol. 2012;44:221–229. - PubMed
-
- Tan N, Liu Y, Zhou YL, He PC, Yang JQ, Luo JF, Chen JY. Contrast medium volume to creatinine clearance ratio: a predictor of contrast-induced nephropathy in the first 72 hours following percutaneous coronary intervention. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2012;79:70–75. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
