Comparison of sirolimus and colchicine treatment on the development of peritoneal fibrozis in rats having peritoneal dialysis
- PMID: 25759780
- PMCID: PMC4342121
- DOI: 10.5152/balkanmedj.2015.15183
Comparison of sirolimus and colchicine treatment on the development of peritoneal fibrozis in rats having peritoneal dialysis
Abstract
Background: Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis is a successful treatment modality for patients with end-stage renal disease. Peritoneal fibrosis (PF) is the most critical complication of long-term peritoneal dialysis (PD).
Aims: In our study, we aimed to compare the effects of colchicine and sirolimus on PF induced by hypertonic peritoneal dialysis solutions in rats.
Study design: Animal experiment.
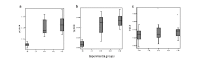
Methods: Twenty-four rats were randomly divided into three groups. The control group received an intraperitoneal injection (ip) of saline. The sirolimus group received the PD solution, plus 1.0 mg/kg/day Rapamune®. The colchicine group received the PD solution ip plus 1.0 mg/kg/day of colchicine. Blood samples were taken to measure the serum levels of VEGF, TGF-β, and TNF-α. Peritoneal tissue samples were taken for histopathological evaluation.
Results: TGF-β and TNF-α values in the sirolimus group were found to be statistically significantly lower than in the control and colchicine groups, but the differences between the control and colchicine groups were not statistically significant. No statistically significant differences were found between the groups regarding the VEGF values. Vascular neogenesis and peritoneal thickness were compared; the values in the sirolimus group were statistically reduced compared to the values in the control group. Mild fibrosis developed in 75% of all animals in the sirolimus group; there was no moderate or severe fibrosis observed. Fibrosis developed to varying degrees in 100% of the animals in the control and colchicine groups.
Conclusion: The present study demonstrates that sirolimus might be beneficial for preventing or delaying the progression of PF and neoangiogenesis. These alterations in the peritoneal membrane may be connected with reduced TNF-α and TGF-β levels.
Keywords: Colchicine; peritoneal dialysis; peritoneal fibrosis; sirolimus.
Figures


References
-
- Sayarlioglu H, Dogan E, Erkoc R, Ozbek H, Bayram I, Sayarlioglu M, et al. The effect of colchicine on the peritoneal membrane. Ren Fail. 2006;28:69–75. - PubMed
-
- Kawaguchi Y, Kawanishi H, Mujais S, Topley N, Oreopoulos DG. Encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis: definition, etiology, diagnosis and treatment. International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis Ad Hoc Committee on Ultrafiltration Management in Peritoneal Dialysis. Perit Dial Int. 2000;20:43–55. - PubMed
-
- Van Westrhenen R, Aten J, Hajji N, de Boer OJ, Kunne C, de Waart DR, et al. Cyclosporin A induces peritoneal fibrosis and angiogenesis during chronic peritoneal exposure to a glucose-based, lactate-buffered dialysis solution in the rat. Blood Purif. 2007;25:466–72. - PubMed
-
- Lin CY, Chen WP, Yang LY, Chen A, Huang TP. Persistent transforming growth factor beta 1 expression may predict peritoneal fibrosis in CAPD patients with frequent peritonitis occurrence. Am J Nephrol. 1998;18:513–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
