Cervical lymph nodes, thyroiditis and ophthalmopathy: the pleomorphic face of an immunoglobulin g4-related disease
- PMID: 25759802
- PMCID: PMC4311305
- DOI: 10.1159/000369204
Cervical lymph nodes, thyroiditis and ophthalmopathy: the pleomorphic face of an immunoglobulin g4-related disease
Abstract
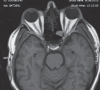
We report a case of immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) presenting with a clinical course suggestive of fibrosing thyroiditis and endocrine ophthalmopathy associated with enlarged cervical lymph nodes. This clinical presentation should prompt a search for associated systemic disorders, including an IgG4-RD. The clue to the exact diagnosis of the underlying disease is histological examination showing an IgG4 plasmatocytic infiltrate in the inflammatory organs involved.
Keywords: Graves’-like orbitopathy; Immunoglobulin G4-related disease; Thyroiditis.
Figures


References
-
- Bartalena L, Baldeschi L, Dickinson A, et al. Consensus statement of the European Group on Graves' Orbitopathy (EUGOGO) on management of GO. Eur J Endocrinol. 2008;158:273–285. - PubMed
-
- Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. Mechanisms of disease: IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:531–551. - PubMed
-
- Fonte R, Pirali B, Chiovato L. Graves'-like orbitopathy in a patient with chronic autoimmune pancreatitis. Thyroid. 2011;21:1389–1392. - PubMed
-
- Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:732–738. - PubMed
-
- Masaki Y, Kurose N, Umehara H. IgG4-related disease: a novel lymphoproliferative disorder discovered and established in Japan in the 21st century. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2011;51:13–20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

