Phaleria macrocarpa Boerl. (Thymelaeaceae) leaves increase SR-BI expression and reduce cholesterol levels in rats fed a high cholesterol diet
- PMID: 25759957
- PMCID: PMC6272643
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules20034410
Phaleria macrocarpa Boerl. (Thymelaeaceae) leaves increase SR-BI expression and reduce cholesterol levels in rats fed a high cholesterol diet
Abstract
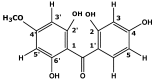
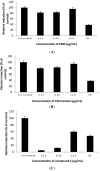
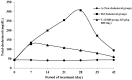
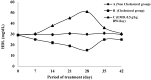
In vitro and in vivo studies of the activity of Phaleria macrocarpa Boerl (Thymelaeaceae) leaves against the therapeutic target for hypercholesterolemia were done using the HDL receptor (SR-BI) and hypercholesterolemia-induced Sprague Dawley rats. The in vitro study showed that the active fraction (CF6) obtained from the ethyl acetate extract (EMD) and its component 2',6',4-trihydroxy-4'-methoxybenzophenone increased the SR-BI expression by 95% and 60%, respectively. The in vivo study has proven the effect of EMD at 0.5 g/kgbw dosage in reducing the total cholesterol level by 224.9% and increasing the HDL cholesterol level by 157% compared to the cholesterol group. In the toxicity study, serum glutamate oxalate transaminase (SGOT) and serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase (SGPT) activity were observed to be at normal levels. The liver histology also proved no toxicity and abnormalities in any of the treatment groups, so it can be categorized as non-toxic to the rat liver. The findings taken together show that P. macrocarpa leaves are safe and suitable as an alternative control and prevention treatment for hypercholesterolemia in Sprague Dawley rats.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Salter A.M., Hayashi R., Al-seeni M., Brown N.F., Bruce J., Sorensen O., Atkinson E.A., Middleton B., Bleackey R.C., Brindley D.N. Effect of hypothyroidism and high-fat feeding on mRNA concentration for the low density lipoprotein receptor and on acyl cholesterol acyl transferase activities in rat liver. J. Biochem. 1991;276:825–832. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

