Phase II DeCOG-study of ipilimumab in pretreated and treatment-naïve patients with metastatic uveal melanoma
- PMID: 25761109
- PMCID: PMC4356548
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118564
Phase II DeCOG-study of ipilimumab in pretreated and treatment-naïve patients with metastatic uveal melanoma
Abstract
Purpose: Up to 50% of patients with uveal melanoma (UM) develop metastatic disease with limited treatment options. The immunomodulating agent ipilimumab has shown an overall survival (OS) benefit in patients with cutaneous metastatic melanoma in two phase III trials. As patients with UM were excluded in these studies, the Dermatologic Cooperative Oncology Group (DeCOG) conducted a phase II to assess the efficacy and safety of ipilimumab in patients with metastatic UM.
Patients and methods: We undertook a multicenter phase II study in patients with different subtypes of metastatic melanoma. Here we present data on patients with metastatic UM (pretreated and treatment-naïve) who received up to four cycles of ipilimumab administered at a dose of 3 mg/kg in 3 week intervals. Tumor assessments were conducted at baseline, weeks 12, 24, 36 and 48 according to RECIST 1.1 criteria. Adverse events (AEs), including immune-related AEs were graded according to National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria (CTC) v.4.0. Primary endpoint was the OS rate at 12 months.
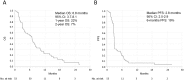
Results: Forty five pretreated (85%) and eight treatment-naïve (15%) patients received at least one dose of ipilimumab. 1-year and 2-year OS rates were 22% and 7%, respectively. Median OS was 6.8 months (95% CI 3.7-8.1), median progression-free survival 2.8 months (95% CI 2.5-2.9). The disease control rate at weeks 12 and 24 was 47% and 21%, respectively. Sixteen patients had stable disease (47%), none experienced partial or complete response. Treatment-related AEs were observed in 35 patients (66%), including 19 grade 3-4 events (36%). One drug-related death due to pancytopenia was observed.
Conclusions: Ipilimumab has very limited clinical activity in patients with metastatic UM. Toxicity was manageable when treated as per protocol-specific guidelines.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01355120.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Diener-West M, Reynolds SM, Agugliaro DJ, Caldwell R, Cumming K, Earle JD, et al. (2005) Development of metastatic disease after enrollment in the COMS trials for treatment of choroidal melanoma: Collaborative Ocular Melanoma Study Group Report No. 26. Arch Ophthalmol 123: 1639–1643. - PubMed
-
- Spendlove HE, Damato BE, Humphreys J, Barker KT, Hiscott PS, Houlston RS (2004) BRAF mutations are detectable in conjunctival but not uveal melanomas. Melanoma Res 14: 449–452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

