Coffee consumption and bladder cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies
- PMID: 25761588
- PMCID: PMC4356958
- DOI: 10.1038/srep09051
Coffee consumption and bladder cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies
Abstract
Controversial results of the association between coffee consumption and bladder cancer (BC) risk were reported among epidemiological studies. Therefore, we conducted this meta-analysis to clarify the association. Relevant studies were identified according to the inclusion criteria. Totally, 34 case-control studies and 6 cohort studies were included in our meta-analysis. The overall odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) between coffee consumption and BC risk was 1.33 (95% CI 1.19 to 1.48). The summary ORs of BC for an increase of 1 cup of coffee per day were 1.05 (95% CI 1.03 to 1.06) for case-control studies and 1.03 (95% CI 0.99 to 1.06) for cohort studies. The overall ORs for male coffee drinkers, female coffee drinkers and coffee drinkers of both gender were 1.31 (95% CI: 1.08 to 1.59), 1.30 (95% CI: 0.87 to 1.96) and 1.35 (95% CI: 1.20 to 1.51). Compared with smokers (OR = 1.24, 95% CI: 0.91 to 1.70), non-smokers had a higher risk (OR = 1.72, 95% CI: 1.25 to 2.35) for BC. Results of this meta-analysis suggested that there was an increased risk between coffee consumption and BC. Male coffee drinkers and non-smoking coffee drinkers were more likely to develop BC.
Figures



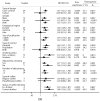
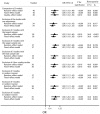
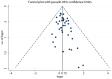
Comment in
-
Coffee consumption and bladder cancer are linked, analysis shows.BMJ. 2015 Mar 18;350:h1477. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h1477. BMJ. 2015. PMID: 25788340 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jemal A. et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61, 69–90 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Leppert J. T. et al. Prevention of bladder cancer: a review. Eur Urol 49, 226–234 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Botteman M. F., Pashos C. L., Redaelli A., Laskin B. & Hauser R. The health economics of bladder cancer. Pharmacoeconomics 21, 1315–1330 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Boyle P. & Levin B. World cancer report 2008. (IARC Press, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2008).
-
- Burger M. et al. Epidemiology and risk factors of urothelial bladder cancer. Eur Urol 63, 234–241 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

