Do Rerevision Rates Differ After First-time Revision of Primary THA With a Cemented and Cementless Femoral Component?
- PMID: 25762017
- PMCID: PMC4586243
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-015-4245-6
Do Rerevision Rates Differ After First-time Revision of Primary THA With a Cemented and Cementless Femoral Component?
Abstract
Background: Worldwide use of cementless fixation for total hip arthroplasty (THA) is on the rise despite some evidence from the world's registries suggesting inferior survivorship compared with cemented techniques. The patterns of bone loss associated with failed cementless and cemented THAs may prejudice the results of future revision procedures; however, this has not been documented.
Questions/purposes: The purpose of this study was to compare (1) the risk for rerevision of first revision THA; (2) the patterns of femoral bone loss at the time of first revision of primary THA; (3) the reasons for first revision of primary THA; and (4) the time to first revision of primary THA between primary cementless and cemented femoral components.
Methods: Primary THAs with cemented (n = 1791) and uncemented (n = 805) femoral components that subsequently sustained first revision of the femoral component were identified from the Danish Hip Arthroplasty Registry (DHR). As of 2012, 120,988 primary THAs and 19,282 revisions were registered in the DHR with completeness of 97% and 90% for primary and revision THA, respectively. Median followup for revisions of primary THA with cemented and cementless femoral component was 4 years (range, 0-17 years) and 2 years (range, 0-16 years), respectively. Survival of first revision THA, with second revision of the femur as outcome, was evaluated using hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence interval (CI) adjusting for potential confounding. All patient- and surgery-related data are collected from Danish medical databases. Recording of bone defects in the DHR is based on surgeons' intraoperative findings.
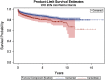
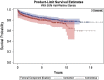
Results: With the numbers studied, we found no differences in the risk of second revision between the overall cohort between cementless and cemented techniques (HR, 1.32; 95% CI, 0.97-1.80; p = 0.076); however, a second revision for any reason was more likely in patients < 70 years old in whom the index arthroplasty was performed using a cementless technique (HR, 1.48; 95% CI, 1.01-2.17; p = 0.046). Increasingly severe femoral bone defects of type II (30% [532 of 1791] versus 13% [104 of 805]; p < 0.001) type III (11% [200 of 1791] versus 2% [12 of 805]; p < 0.001) and type IV (1% [26 of 1791] versus 0.4% [three of 805]; p = 0.016) were more frequent at revisions of cemented femoral components compared with cementless femoral components. Indications for first revision differed between primary cemented and uncemented femoral components, because a larger proportion of cemented femoral components was revised as a result of aseptic loosening compared with cementless femoral components (74% [1329 of 1791] versus 25% [197 of 805]; p < 0.001), whereas a larger proportion of cementless femoral components was revised as a result of a fracture compared with cemented femoral components (46% [371 of 805] versus 10% [168 of 1791]; p < 0.001). Failure before 5 years was more likely in cementless femoral components than cemented femoral components (91% [733 of 805] versus 44% [749 of 1791], p < 0.001).
Conclusions: We found no differences in the risk of second revision in the overall cohort between cementless and cemented techniques; however, we observed an increased risk for rerevision THA performed on patients < 70 years whose index THAs were performed using cementless components when looking at all causes for revision, even after adjusting for the most likely confounding factors. Our data suggest that increased use of cementless fixation in primary THA may lead to inferior survivorship of first revision THA.
Level of evidence: Level III, therapeutic study.
Figures
Comment in
-
CORR Insights(®): Do Rerevision Rates Differ After First-time Revision of Primary THA With a Cemented and Cementless Femoral Component?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015 Nov;473(11):3399-400. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4294-x. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015. PMID: 25894809 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Andersen TF, Madsen M, Jørgensen J, Mellemkjoer L, Olsen JH. The Danish National Hospital Register. A valuable source of data for modern health sciences. Dan Med Bull. 1999;46:263–268. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. International Classification of Diseases (ICD). Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

