Making sense of hematopoietic stem cell niches
- PMID: 25762174
- PMCID: PMC4408288
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-09-570192
Making sense of hematopoietic stem cell niches
Abstract
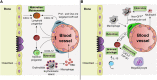
The hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) niche commonly refers to the pairing of hematopoietic and mesenchymal cell populations that regulate HSC self-renewal, differentiation, and proliferation. Anatomic localization of the niche is a dynamic unit from the developmental stage that allows proliferating HSCs to expand before they reach the bone marrow where they adopt a quiescent phenotype that protects their integrity and functions. Recent studies have sought to clarify the complexity behind the HSC niche by assessing the contributions of specific cell populations to HSC maintenance. In particular, perivascular microenvironments in the bone marrow confer distinct vascular niches that regulate HSC quiescence and the supply of lineage-committed progenitors. Here, we review recent data on the cellular constituents and molecular mechanisms involved in the communication between HSCs and putative niches.
© 2015 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures


References
-
- Till JE, McCulloch EA. A direct measurement of the radiation sensitivity of normal mouse bone marrow cells. Radiat Res. 1961;14:213–222. - PubMed
-
- Becker AJ, McCulloch EA, Till JE. Cytological demonstration of the clonal nature of spleen colonies derived from transplanted mouse marrow cells. Nature. 1963;197:452–454. - PubMed
-
- Siminovitch L, McCulloch EA, Till JE. The Distribution of Colony-Forming Cells among Spleen Colonies. J Cell Physiol. 1963;62:327–336. - PubMed
-
- Cheng T, Rodrigues N, Shen H, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell quiescence maintained by p21cip1/waf1. Science. 2000;287(5459):1804–1808. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

