Tyrosine Kinase 2-mediated Signal Transduction in T Lymphocytes Is Blocked by Pharmacological Stabilization of Its Pseudokinase Domain
- PMID: 25762719
- PMCID: PMC4409266
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.619502
Tyrosine Kinase 2-mediated Signal Transduction in T Lymphocytes Is Blocked by Pharmacological Stabilization of Its Pseudokinase Domain
Abstract
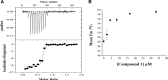
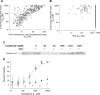
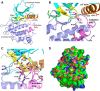
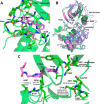
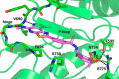
Inhibition of signal transduction downstream of the IL-23 receptor represents an intriguing approach to the treatment of autoimmunity. Using a chemogenomics approach marrying kinome-wide inhibitory profiles of a compound library with the cellular activity against an IL-23-stimulated transcriptional response in T lymphocytes, a class of inhibitors was identified that bind to and stabilize the pseudokinase domain of the Janus kinase tyrosine kinase 2 (Tyk2), resulting in blockade of receptor-mediated activation of the adjacent catalytic domain. These Tyk2 pseudokinase domain stabilizers were also shown to inhibit Tyk2-dependent signaling through the Type I interferon receptor but not Tyk2-independent signaling and transcriptional cellular assays, including stimulation through the receptors for IL-2 (JAK1- and JAK3-dependent) and thrombopoietin (JAK2-dependent), demonstrating the high functional selectivity of this approach. A crystal structure of the pseudokinase domain liganded with a representative example showed the compound bound to a site analogous to the ATP-binding site in catalytic kinases with features consistent with high ligand selectivity. The results support a model where the pseudokinase domain regulates activation of the catalytic domain by forming receptor-regulated inhibitory interactions. Tyk2 pseudokinase stabilizers, therefore, represent a novel approach to the design of potent and selective agents for the treatment of autoimmunity.
Keywords: Allosteric Regulation; Janus Kinase (JAK); Molecular Pharmacology; Pseudokinase; Signal Transduction; Structural Biology.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Miossec P., Kolls J.K. (2012) Targeting IL-17 and TH17 cells in chronic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 11, 763–776 - PubMed
-
- Volpe E., Servant N., Zollinger R., Bogiatzi S. I., Hupé P., Barillot E., Soumelis V. (2008) A critical function for transforming growth factor-β, interleukin 23 and proinflammatory cytokines in driving and modulating human T(H)-17 responses. Nat. Immunol. 9, 650–657 - PubMed
-
- Sandborn W. J., Gasink C., Gao L. L., Blank M. A., Johanns J., Guzzo C., Sands B. E., Hanauer S. B., Targan S., Rutgeerts P., Ghosh S., de Villiers W. J., Panaccione R., Greenberg G., Schreiber S., Lichtiger S., Feagan B. G., and CERTIFI Study Group (2012) Ustekinumab induction and maintenance therapy in refractory Crohn's disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 367, 1519–1528 - PubMed
-
- Strober B. E., Crowley J. J., Yamauchi P. S., Olds M., Williams D. A. (2011) Efficacy and safety results from a phase III, randomized controlled trial comparing the safety and efficacy of briakinumab with etanercept and placebo in patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 165, 661–668 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

