Compartmentalized accumulation of cAMP near complexes of multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4) and cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) contributes to drug-induced diarrhea
- PMID: 25762723
- PMCID: PMC4416832
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.605410
Compartmentalized accumulation of cAMP near complexes of multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4) and cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) contributes to drug-induced diarrhea
Abstract
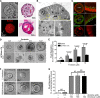
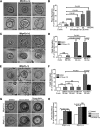
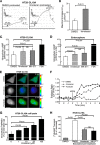
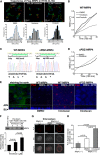
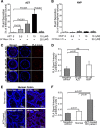
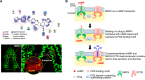
Diarrhea is one of the most common adverse side effects observed in ∼7% of individuals consuming Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drugs. The mechanism of how these drugs alter fluid secretion in the gut and induce diarrhea is not clearly understood. Several drugs are either substrates or inhibitors of multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4), such as the anti-colon cancer drug irinotecan and an anti-retroviral used to treat HIV infection, 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine (AZT). These drugs activate cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)-mediated fluid secretion by inhibiting MRP4-mediated cAMP efflux. Binding of drugs to MRP4 augments the formation of MRP4-CFTR-containing macromolecular complexes that is mediated via scaffolding protein PDZK1. Importantly, HIV patients on AZT treatment demonstrate augmented MRP4-CFTR complex formation in the colon, which defines a novel paradigm of drug-induced diarrhea.
Keywords: ABC Transporter; Chloride Channel; Chloride Transport; Cyclic AMP (cAMP); Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR); Drug-induced Secretory Diarrhea; Enterosphere; MRP4; Multidrug Transporter; PDZ Domain.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
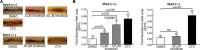
References
-
- Chassany O., Michaux A., Bergmann J. F. (2000) Drug-induced diarrhoea. Drug Saf. 22, 53–72 - PubMed
-
- Ratnaike R. N., Jones T. E. (1998) Mechanisms of drug-induced diarrhoea in the elderly. Drugs Aging 13, 245–253 - PubMed
-
- Kunzelmann K., Mall M. (2002) Electrolyte transport in the mammalian colon: mechanisms and implications for disease. Physiol. Rev. 82, 245–289 - PubMed
-
- Schuetz J. D., Connelly M. C., Sun D., Paibir S. G., Flynn P. M., Srinivas R. V., Kumar A., Fridland A. (1999) MRP4: a previously unidentified factor in resistance to nucleoside-based antiviral drugs. Nat. Med. 5, 1048–1051 - PubMed
-
- Pizzolato J. F., Saltz L. B. (2003) The camptothecins. Lancet 361, 2235–2242 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

