Murine Gammaherpesvirus 68 ORF48 Is an RTA-Responsive Gene Product and Functions in both Viral Lytic Replication and Latency during In Vivo Infection
- PMID: 25762743
- PMCID: PMC4442421
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00406-15
Murine Gammaherpesvirus 68 ORF48 Is an RTA-Responsive Gene Product and Functions in both Viral Lytic Replication and Latency during In Vivo Infection
Abstract
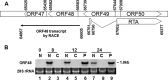
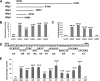
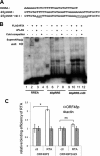
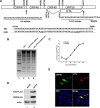
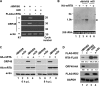
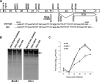
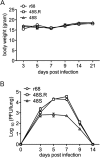
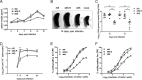
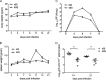
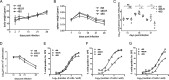
Replication and transcription activator (RTA) of gammaherpesvirus is an immediate early gene product and regulates the expression of many downstream viral lytic genes. ORF48 is also conserved among gammaherpesviruses; however, its expression regulation and function remained largely unknown. In this study, we characterized the transcription unit of ORF48 from murine gammaherpesvirus 68 (MHV-68) and analyzed its transcriptional regulation. We showed that RTA activates the ORF48 promoter via an RTA-responsive element (48pRRE). RTA binds to 48pRRE directly in vitro and also associates with ORF48 promoter in vivo. Mutagenesis of 48pRRE in the context of the viral genome demonstrated that the expression of ORF48 is activated by RTA through 48pRRE during de novo infection. Through site-specific mutagenesis, we generated an ORF48-null virus and examined the function of ORF48 in vitro and in vivo. The ORF48-null mutation remarkably reduced the viral replication efficiency in cell culture. Moreover, through intranasal or intraperitoneal infection of laboratory mice, we showed that ORF48 is important for viral lytic replication in the lung and establishment of latency in the spleen, as well as viral reactivation from latency. Collectively, our study identified ORF48 as an RTA-responsive gene and showed that ORF48 is important for MHV-68 replication both in vitro and in vivo.
Importance: The replication and transcription activator (RTA), conserved among gammaherpesviruses, serves as a molecular switch for the virus life cycle. It works as a transcriptional regulator to activate the expression of many viral lytic genes. However, only a limited number of such downstream genes have been uncovered for MHV-68. In this study, we identified ORF48 as an RTA-responsive gene of MHV-68 and mapped the cis element involved. By constructing a mutant virus that is deficient in ORF48 expression and through infection of laboratory mice, we showed that ORF48 plays important roles in different stages of viral infection in vivo. Our study provides insights into the transcriptional regulation and protein function of MHV-68, a desired model for studying gammaherpesviruses.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rta of murine gammaherpesvirus 68 reactivates the complete lytic cycle from latency.J Virol. 2000 Apr;74(8):3659-67. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.8.3659-3667.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10729142 Free PMC article.
-
Replication and transcription activator (RTA) of murine gammaherpesvirus 68 binds to an RTA-responsive element and activates the expression of ORF18.J Virol. 2011 Nov;85(21):11338-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00561-11. Epub 2011 Aug 17. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21849436 Free PMC article.
-
Function of Rta is essential for lytic replication of murine gammaherpesvirus 68.J Virol. 2001 Oct;75(19):9262-73. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.19.9262-9273.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11533188 Free PMC article.
-
The Rta/Orf50 transactivator proteins of the gamma-herpesviridae.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007;312:71-100. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-34344-8_3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17089794 Review.
-
Lytic cycle switches of oncogenic human gammaherpesviruses.Adv Cancer Res. 2007;97:81-109. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(06)97004-3. Adv Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17419942 Review.
Cited by
-
ORF48 is required for optimal lytic replication of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Aug 26;20(8):e1012081. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012081. eCollection 2024 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39186813 Free PMC article.
-
The C-Terminus of Epstein-Barr Virus BRRF2 Is Required for its Proper Localization and Efficient Virus Production.Front Microbiol. 2017 Jan 31;8:125. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00125. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28197146 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of murine herpesvirus-68 replication by IFN-gamma in macrophages is counteracted by the induction of SOCS1 expression.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Aug 3;14(8):e1007202. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007202. eCollection 2018 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 30075008 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-Like Vesicles of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Activate Lytic Replication by Triggering Differentiation Signaling.J Virol. 2017 Jul 12;91(15):e00362-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00362-17. Print 2017 Aug 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28515293 Free PMC article.
-
RNF213 modulates γ-herpesvirus infection and reactivation via targeting the viral Replication and Transcription Activator.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Mar 21;120(12):e2218825120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2218825120. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 36917666 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

