Circulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor concentrations and the risk of cardiovascular disease in the community
- PMID: 25762803
- PMCID: PMC4392437
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.114.001544
Circulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor concentrations and the risk of cardiovascular disease in the community
Erratum in
-
Circulating Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Concentrations and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in the Community.J Am Heart Assoc. 2016 Jul 18;5(7):e002098. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.002098. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016. PMID: 27431646 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a pleiotropic peptide involved in maintaining endothelial integrity. It is unknown if circulating BDNF levels are associated with risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
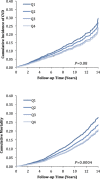
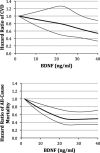
Methods and results: We prospectively investigated the association of circulating BDNF levels with cardiovascular events and mortality in 3687 participants (mean age 65 years, 2068 women) from the Framingham Heart Study (FHS). Using a common nonsynonomous single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the BDNF gene (rs6265), we then performed a Mendelian randomization experiment in the CARDIoGRAM (Coronary ARtery DIsease Genome-Wide Replication And Meta-Analysis) consortium (>22,000 coronary artery disease [CAD] cases, >60,000 controls) to investigate whether SNP rs6265 was associated with CAD in CARDIoGRAM and, if so, whether the effect estimate differed from that predicted based on FHS data. On follow-up (median 8.9 years), 467 individuals (261 women) in FHS experienced a CVD event, and 835 (430 women) died. In multivariable-adjusted Cox regression, serum BDNF was associated inversely with CVD risk (hazard ratio [HR] per 1-SD increase 0.88, 95% CI 0.80 to 0.97, P=0.01) and with mortality (HR 0.87, 95% CI 0.80 to 0.93, P=0.0002). SNP rs6265 was associated with BDNF concentrations (0.772 ng/mL increase per minor allele copy) in FHS. In CARDIoGRAM, SNP rs6265 was associated with CAD (odds ratio 0.957, 95% CI 0.923 to 0.992), a magnitude consistent with the predicted effect (HR per minor allele copy 0.99, 95% CI 0.98 to 1.0; P=0.06 for difference between predicted and observed effect).
Conclusion: Higher serum BDNF is associated with a decreased risk of CVD and mortality. Mendelian randomization suggests a causal protective role of BDNF in the pathogenesis of CVD.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; cardiovascular disease; growth factors; mortality; risk factors.
© 2015 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures

References
-
- Donovan MJ, Lin MI, Wiegn P, Ringstedt T, Kraemer R, Hahn R, Wang S, Ibanez CF, Rafii S, Hempstead BL. Brain derived neurotrophic factor is an endothelial cell survival factor required for intramyocardial vessel stabilization. Development. 2000; 127:4531-4540. - PubMed
-
- Okada S, Yokoyama M, Toko H, Tateno K, Moriya J, Shimizu I, Nojima A, Ito T, Yoshida Y, Kobayashi Y, Katagiri H, Minamino T, Komuro I. Brain‐derived neurotrophic factor protects against cardiac dysfunction after myocardial infarction via a central nervous system‐mediated pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012; 32:1902-1909. - PubMed
-
- Jiang H, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Chen ZY. Association of plasma brain‐derived neurotrophic factor and cardiovascular risk factors and prognosis in angina pectoris. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011; 415:99-103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

