Co-occurrence of multiple sclerosis and Thomsen's myotonia: a report of two cases
- PMID: 25764257
- PMCID: PMC4370440
Co-occurrence of multiple sclerosis and Thomsen's myotonia: a report of two cases
Abstract
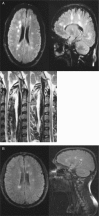
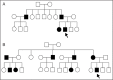
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a common demyelinating disease of the central nervous system in which an abnormal immune system response results in damage to the myelin sheaths surrounding nerves. The etiology of MS remains elusive, although it has been suggested to be influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. Here, we report two exceptional cases of patients affected by both MS and Thomsen's myotonia. Electromyography and MRI scans confirmed the presence of both diseases in the referred cases. Although the mechanisms underlying the co-occurrence of MS and Thomsen's disease are unclear, we have endeavored to offer plausible explanations for it.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fluctuating clinical myotonia and weakness from Thomsen's disease occurring only during pregnancies.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1999 Jun;101(2):133-6. doi: 10.1016/s0303-8467(99)00019-0. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1999. PMID: 10467912
-
[Steinert's myotonic dystrophy and Thomsen's congenital myotonia. Observation of a family (author's transl)].Riv Patol Nerv Ment. 1979 Jul-Aug;100(4):209-19. Riv Patol Nerv Ment. 1979. PMID: 555540 Italian.
-
Successful dantrolene sodium treatment of a patient with myotonia congenita (Thomsen's disease).Acta Paediatr Jpn. 1991 Oct;33(5):668-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-200x.1991.tb01884.x. Acta Paediatr Jpn. 1991. PMID: 1799124
-
[Case history contribution and findings in Thomsen's myotonia congenita].Arch Kinderheilkd. 1966 Aug;174(3):365-79. Arch Kinderheilkd. 1966. PMID: 5994000 German. No abstract available.
-
[Relapsing-remitting inflammatory disease of the central nervous system with normal MRI: multiple sclerosis or phenocopy in a series of 15 patients].Rev Neurol (Paris). 2003 Apr;159(4):397-404. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2003. PMID: 12773868 Review. French.
Cited by
-
A case report of recessive myotonia congenita and early onset cognitive impairment: Is it a causal or casual link?Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Jun;97(22):e10785. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010785. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29851785 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-channel registration of fractional anisotropy and T1-weighted images in the presence of atrophy: application to multiple sclerosis.Funct Neurol. 2015 Oct-Dec;30(4):245-56. doi: 10.11138/fneur/2015.30.4.245. Funct Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26727703 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ebers GC, Bulman DE, Sadovnick AD, et al. A population-based study of multiple sclerosis in twins. N Engl J Med. 1986;315:1638–1642. - PubMed
-
- Esteban J, Neumeyer AM, McKenna-Yasek D, et al. Identification of two mutations and a polymorphism in the chloride channel CLCN-1 in patients with Becker’s generalized myotonia. Neurogenetics. 1998;1:185–188. - PubMed
-
- Farbu E, Søfteland E, Bindoff LA. Anaesthetic complications associated with myotonia congenita: case study and comparison with other myotonic disorders. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2003;47:630–634. - PubMed
-
- Parasivam S, Krupa M, Slee M, et al. Clinical, electro-physiological and genetic features of a large Australian family with paramyotonia congenita. Med J Aust. 2009;190:334–336. - PubMed
-
- Portaro S, Musumeci O, Rizzo V, et al. Stiffness as a presenting symptom of an odd clinical condition caused by multiple sclerosis and myotonia congenita. Neuromuscul Disord. 2013;23:52–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
