Toll-interacting protein contributes to mortality following myocardial infarction through promoting inflammation and apoptosis
- PMID: 25765712
- PMCID: PMC4500373
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13130
Toll-interacting protein contributes to mortality following myocardial infarction through promoting inflammation and apoptosis
Abstract
Background and purpose: Toll-interacting protein (Tollip) is an endogenous inhibitor of toll-like receptors, a superfamily that plays a pivotal role in various pathological conditions, including myocardial infarction (MI). However, the exact role of Tollip in MI remains unknown.
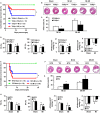
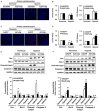
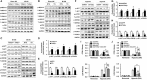
Experimental approach: MI models were established in Tollip knockout (KO) mice, mice with cardiac-specific overexpression of human Tollip gene and in their Tollip(+/+) and non-transgenic controls respectively. The effects of Tollip on MI were evaluated by mortality, infarct size and cardiac function. Hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte damage was investigated in vitro to confirm the role of Tollip in heart damage.
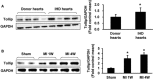
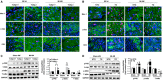
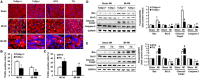
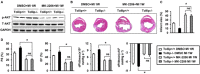
Key results: Tollip expression was dramatically up-regulated in human ischaemic hearts and infarcted mice hearts. MI-induced mortality, infarct size and cardiac dysfunction were decreased in Tollip-KO mice compared with Tollip(+/+) controls. Ischaemic hearts from Tollip-KO mice exhibited decreased inflammatory cell infiltration and reduced NF-κB activation. Tollip depletion also alleviated myocardial apoptosis by down-regulating pro-apoptotic protein levels and up-regulating anti-apoptotic protein expressions in infarct border zone. Conversely, MI effects were exacerbated in mice with cardiac-specific Tollip overexpression. This aggravated MI injury by Tollip in vivo was confirmed with in vitro assays. Inhibition of Akt signalling was associated with the detrimental effects of Tollip on MI injury; activation of Akt largely reversed the deleterious effects of Tollip on MI-induced cardiomyocyte death.
Conclusions and implications: Tollip promotes inflammatory and apoptotic responses after MI, leading to increased mortality and aggravated cardiac dysfunction. These findings suggest that Tollip may serve as a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of MI.
© 2015 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulatory role of CARD3 in left ventricular remodelling and dysfunction after myocardial infarction.Basic Res Cardiol. 2015 Nov;110(6):56. doi: 10.1007/s00395-015-0515-4. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Basic Res Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26463597
-
Tollip is a critical mediator of cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury.J Pathol. 2015 Oct;237(2):249-62. doi: 10.1002/path.4565. Epub 2015 Jun 22. J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26011492
-
Vinexin-β exacerbates cardiac dysfunction post-myocardial infarction via mediating apoptotic and inflammatory responses.Clin Sci (Lond). 2015 Jun;128(12):923-36. doi: 10.1042/CS20140648. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015. PMID: 25658191
-
Toll-interacting protein impacts on inflammation, autophagy, and vacuole trafficking in human disease.J Mol Med (Berl). 2021 Jan;99(1):21-31. doi: 10.1007/s00109-020-01999-4. Epub 2020 Oct 31. J Mol Med (Berl). 2021. PMID: 33128579 Review.
-
Toll-Interacting Protein in Pulmonary Diseases. Abiding by the Goldilocks Principle.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021 May;64(5):536-546. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0470TR. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33233920 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tollip Negatively Regulates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell-Mediated Neointima Formation by Suppressing Akt-Dependent Signaling.J Am Heart Assoc. 2018 Jun 10;7(12):e006851. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.006851. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. PMID: 29887521 Free PMC article.
-
Role of miRNA-324-5p-Modified Adipose-Derived Stem Cells in Post-Myocardial Infarction Repair.Int J Stem Cells. 2021 Aug 30;14(3):298-309. doi: 10.15283/ijsc21025. Int J Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 34158416 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-369 attenuates hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and inflammation via targeting TRPV3.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021 Jan 15;54(3):e10550. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X202010550. eCollection 2021. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021. PMID: 33470394 Free PMC article.
-
Anshen Shumai Decoction inhibits post-infarction inflammation and myocardial remodeling through suppression of the p38 MAPK/c-FOS/EGR1 pathway.J Mol Histol. 2024 Aug;55(4):437-454. doi: 10.1007/s10735-024-10214-4. Epub 2024 Jun 14. J Mol Histol. 2024. PMID: 38874870
-
Regulation of Key Immune-Related Genes in the Heart Following Burn Injury.J Pers Med. 2022 Jun 20;12(6):1007. doi: 10.3390/jpm12061007. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35743792 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baldi A, Abbate A, Bussani R, Patti G, Melfi R, Angelini A, et al. Apoptosis and post-infarction left ventricular remodeling. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2002;34:165–174. - PubMed
-
- Bulut Y, Faure E, Thomas L, Equils O, Arditi M. Cooperation of Toll-like receptor 2 and 6 for cellular activation by soluble tuberculosis factor and Borrelia burgdorferi outer surface protein A lipoprotein: role of Toll-interacting protein and IL-1 receptor signaling molecules in Toll-like receptor 2 signaling. J Immunol. 2001;167:987–994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

